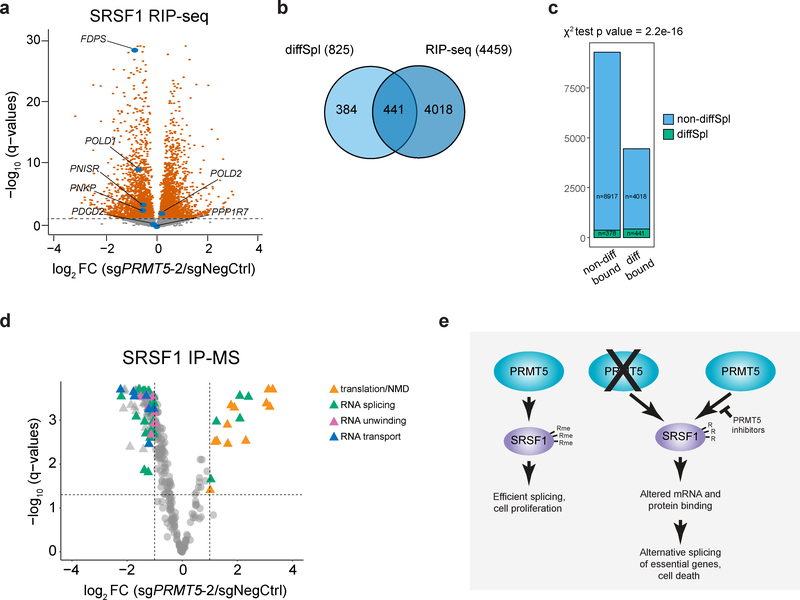
Figure 7. PRMT5 depletion impacts SRSF1 binding to mRNAs and proteins.
a, Differential binding of SRSF1 to mRNAs upon PRMT5 KD (differentially bound mRNAs are represented by orange color, q-value < 0.05). mRNAs of 13754 genes were identified of which 4459 were differentially bound. b, Overlap of differentially spliced genes with the genes, which mRNAs are differentially bound by SRSF1 upon PRMT5 KD. c, Distribution of differentially spliced genes among the genes with differentially or non-differentially bound mRNAs. d, Differential binding of SRSF1 to proteins upon PRMT5 KD. Dashed lines indicate the chosen thresholds of 2-fold change and q-value of 0.05. Total of 350 binding partners were quantified, and 162 significantly differentially bound proteins are indicated with triangles. The most enriched functional groups of proteins among the differential interactors are indicated with color. e, Proposed model for the essential function of PRMT5. PRMT5 methylates SRSF1 at three arginine sites, which are important for the function of SRSF1 in splicing regulation. Loss of SRSF1 methylation leads to altered binding of SRSF1 to mRNA and proteins, differential alternative splicing of multiple essential genes and, consequently, cell death. RIP-sequencing and SRSF1 IP-MS experiments were performed using 3 independently transduced samples of each sgRNA. The source data for the figure is available in Supplementary Tables 3 and 4.