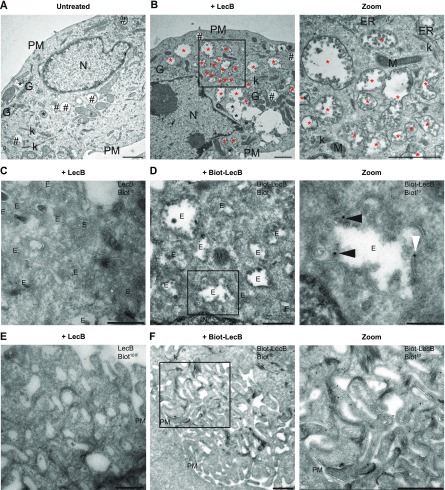
Figure 4. The cytotoxic effect of LecB is preceded by the formation of intraluminal vesicle-containing vacuoles.
(A, B) NHKs were incubated with 5 μg/ml LecB and processed for conventional electron microscopy at 12 h post-incubation. (A, B) Representative electrographs of the untreated (A) and LecB-treated (B) cells. Black hashtags point at Category 1 vacuoles, whereas black and red asterisks indicate Category 2 and Category 3 vacuoles, respectively. Zoomed image of panel (B) shows a higher magnification of the Category 3 vacuoles containing intraluminal vesicles. Scale bars: 1 μm. (C, D, E, F) Cells treated with 5 μg/ml biotinylated LecB or un-tagged LecB for 12 h were subjected to immuno-EM. (C, E) Control staining showing no aspecific antibody binding. (D) LecB localises in internal vesicles, either in the lumen (panel [D] zoom, black arrowheads) or at the limiting membrane (white arrowheads). (F) LecB localisation at the plasma membrane, in the ruffle-like region. Scale bars: 500 nm. Scale bar zoom panel (D): 200 nm. E, endosome; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; G, Golgi apparatus; k, keratin; M, mitochondrion; N, nucleus; PM, plasma membrane.