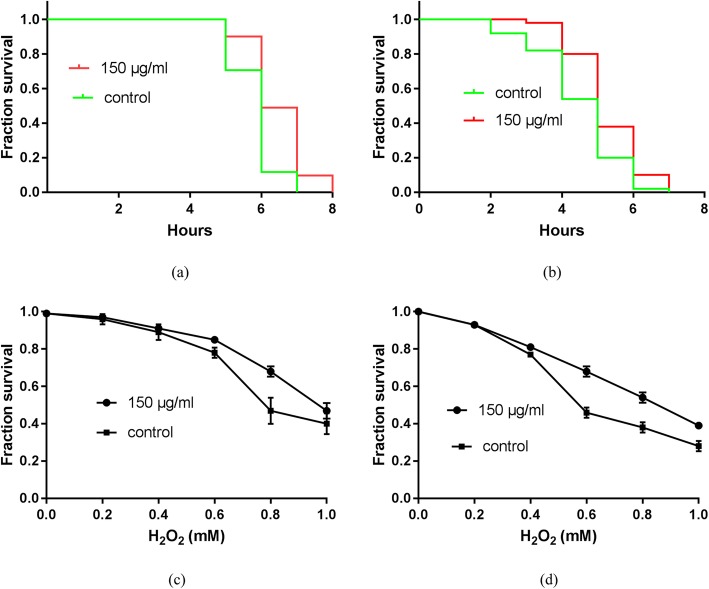
Fig. 2.
The effect of JPYW on stress resistance in C. elegans N2 worms. a Heat stress resistance in wild-type larvae. Wild-type worms that were incubated at a constant temperature (37 °C) were pretreated with 150 μg/ml JPYW or vehicle control (1% DMSO). Survival was assessed every hour after heat stress treatment. JPYW significantly prolonged the lifespan of wild-type worms under heat stress compared to the vehicle control (n = 50–55, P < 0.05). b Heat stress resistance in aged C. elegans N2 worms. Aged worms that were incubated at a constant temperature (37 °C) were pretreated with 150 μg/ml JPYW or vehicle control (1% DMSO). Survival was assessed every hour after heat stress treatment. JPYW treatment significantly prolonged the lifespan of aged wild-type worms under heat stress compared to the control treatment (n = 50–55, P < 0.05). c Oxidative stress resistance in C. elegans N2 worms. Wild-type worms were pretreated with 150 μg/ml JPYW or vehicle control (1% DMSO) and were exposed to various concentrations of hydrogen peroxide (0, 0.2, 0.4, 0.6, 0.8, and 1 mM). Survival was assessed after 15 h of each treatment. d Oxidative stress resistance in aged C. elegans N2 worms. Aged worms were pretreated with 150 μg/ml JPYW or vehicle control (1% DMSO) and were exposed to various concentrations of hydrogen peroxide (0, 0.2, 0.4, 0.6, 0.8, and 1 mM). Survival was assessed after 15 h of each treatment