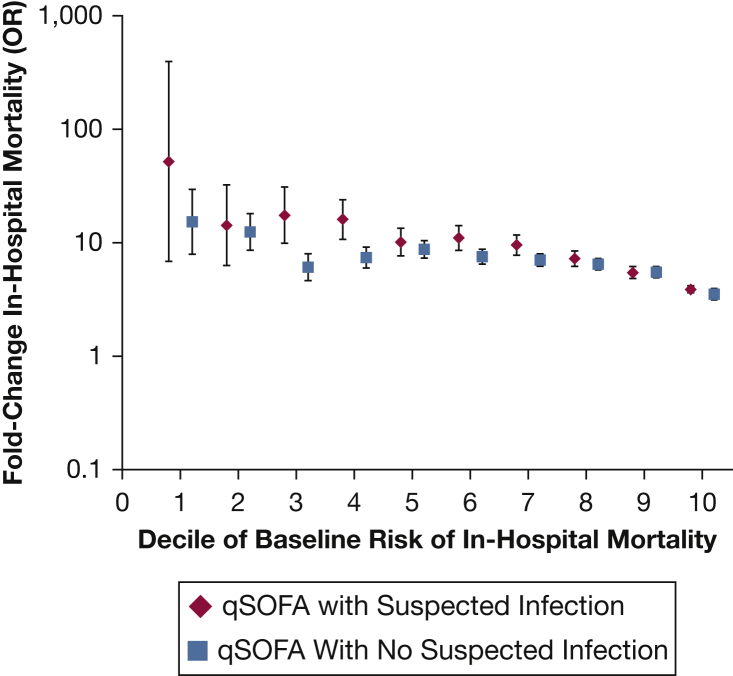
Figure 2.
Fold change in rate of in-hospital mortality by deciles of baseline risk of death for ≥ 2 qSOFA criteria vs < 2 qSOFA criteria in patients with and without suspected infection on admission. The x axis divides the cohort into deciles of baseline risk, which were created on the basis of age, sex, race, and Elixhauser Comorbidity Index. The y axis shows the fold increase in the odds of death (log scale) for a patient with suspected infection or without suspected infection who meets ≥ 2 qSOFA criteria for each decile of risk. For example, a patient who falls into the 5th decile of baseline risk (based on moderate burden of comorbidities) with suspected infection (eg, pneumonia) has an approximately 10-fold increased odds of death if he has ≥ 2 qSOFA criteria vs < 2 qSOFA criteria. He has similarly increased odds of death with ≥ 2 qSOFA criteria vs < 2 qSOFA criteria even if he did not have suspected infection. See Figure 1 legend for expansion of abbreviation.