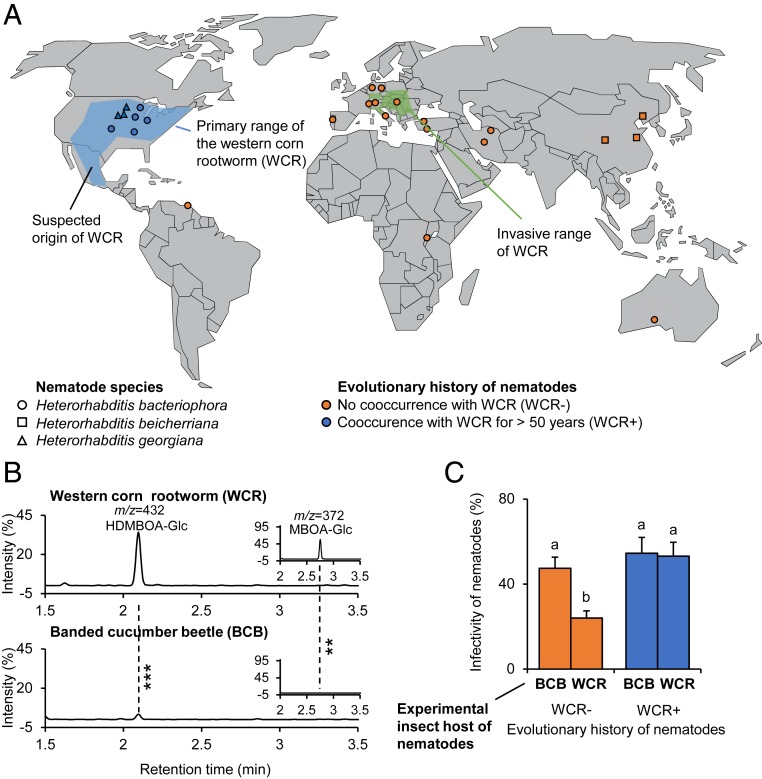
Fig. 1.
Entomopathogenic nematodes from the primary range of the benzoxazinoid-sequestering WCR are more infective toward the WCR than the nonsequestering BCB. (A) World map showing the origin of the collected entomopathogenic nematode strains together with the primary and invasive ranges of the WCR, a specialized maize herbivore (WCR; data from 2012). Note that nematode strains from the invasive range do not share any evolutionary history with WCR, as they were collected before invasion. For detailed information about the different strains, refer to SI Appendix, Table S1. (B) Chromatograms of plant-derived benzoxazinoids in the body of WCR (Top) and the BCB (Bottom), a generalist root herbivore which does not sequester benzoxazinoids and is mainly present in Central America, Mexico, and the Southern United States, outside of the nematode sampling range. Asterisks indicate significant differences between herbivore species (**P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001). For quantitative comparisons, refer to SI Appendix, Fig. S1. (C) Infectivity of nematodes toward WCR and BCB. Infectivity is shown for nematodes with an evolutionary history with WCR of more than 50 y (blue) and nematodes without evolutionary history with WCR (orange). EMMeans and SEs derived from statistical models (Dataset S1) are shown. Different letters indicate significant differences between treatments (false discovery rate corrected P < 0.05).