Fig. 2.
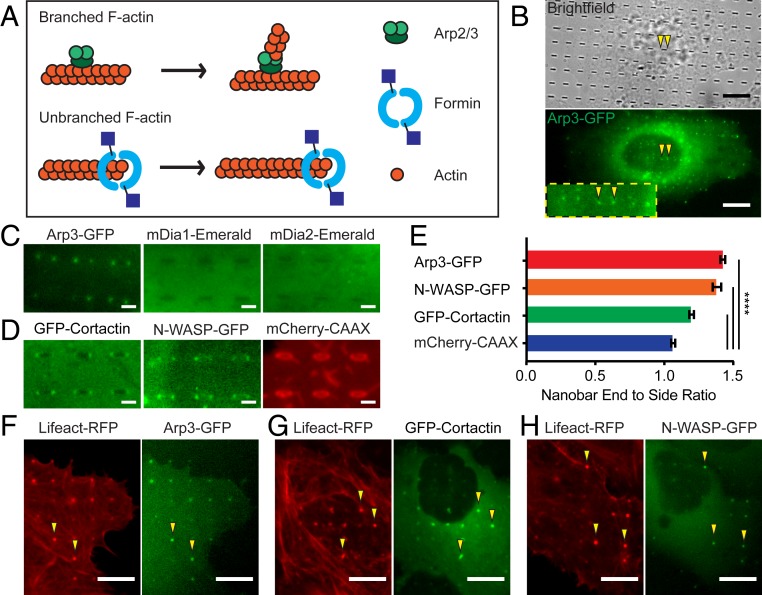
Nanostructure-induced F-actin is branched F-actin nucleated by Arp2/3. (A) A schematic illustration of actin nucleators, Arp2/3 and formin, involved in polymerizing branched and linear actin filaments, respectively. (B) Live-cell imaging shows that Arp3-GFP strongly accumulates at the ends of nanobars (arrowheads). (C) Zoomed-in fluorescence images of Arp3-GFP, mDia1-Emerald, or mDia2-Emerald in U2OS cells show that only Arp3-GFP accumulates at the ends of nanobars (see SI Appendix, Fig. S2B for the full images). (D) Zoomed-in fluorescence images of GFP-Cortactin, N-WASP-GFP, and mCherry-CAAX show strong accumulation of GFP-Cortactin and N-WASP-GFP to the ends of nanobars (see SI Appendix, Fig. S2C for the full images). (E) Quantification of the nanobar-end-to-side ratio for Arp3-GFP, N-WASP-GFP, GFP-Cortactin, and mCherry-CAAX, n = 789 to 2,746 nanobars (see SI Appendix, Table S2 for detailed statistics). (F–H) Live-cell fluorescence images of cotransfected cells show that F-actin marker Lifeact colocalizes with Arp3 (F), Cortactin (G), and N-WASP (H). Welch’s t test, P value indicated in E, ****P < 0.0001; error bars represent SEM. (Scale bars, 10 μm [B] and 2 μm [C and D].)