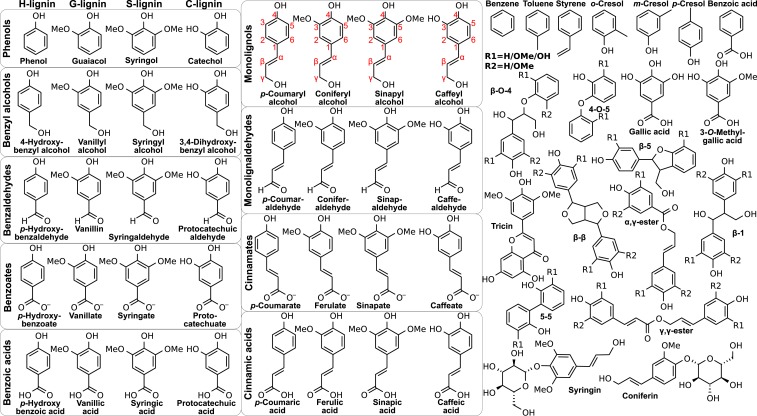
Fig. 1.
LRCs examined, grouped by their chemistry. On the left are monomeric (single aromatic ring) compounds including monolignols and derivatives encountered via lignin deconstruction processes (H, G, S, and C substitutions from left to right). Other compounds enriched in fragmented lignin streams are also considered, including dimeric LRCs with monomer-dependent R1 and R2 groups, a representative flavonoid (tricin), glucosides (coniferin and syringin), and other aromatics (e.g., cresols). LRCs that can be derived from high-severity processes, such as benzene, are also considered. The red monolignol labeling defines lignin carbon nomenclature.