Fig. 4. Fn nanofiber scaffolds promoted native dermal and epidermal architecture recovery.
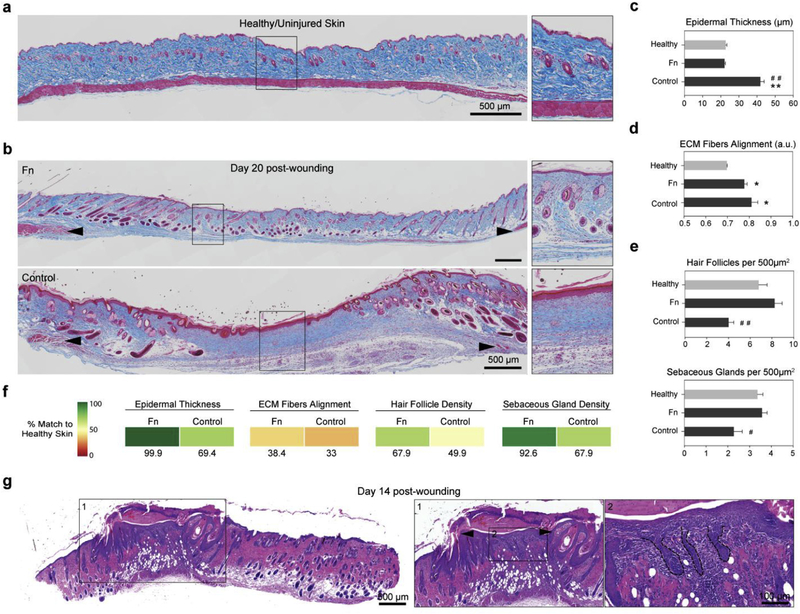
(a) Masson’s trichrome staining of healthy native tissue sections was performed to establish the design criterion for successful skin tissue restoration. We measured an epidermal thickness of ~20 μm, ECM fiber alignment of ~0.36 (a.u.) as well as ~7 hair follicles and ~3.5 sebaceous glands per surface area of 500 μm2 (c–e). (b) Representative stains of skin tissues with different treatment conditions 20 days post wounding. Black arrowheads indicate original wound edges. Insets demonstrate recovery of epidermal thickness and presence of skin appendages at the center of the wound in the Fn-treated tissue, in contrast with the control group. (c) Epidermal thickness measurements showed that Fn nanofiber dressings restored tissue close to its healthy state, whereas the control had a statistically significant increase in thickness. (d) ECM fiber alignment was used to quantify native tissue (characterized by a basket-woven structure) and scarred tissue (aligned fiber bundles) where 0 is perfectly isotropic and 1 is perfectly anisotropic. Analysis revealed that all recovering tissues were more aligned than native skin, with the Fn condition closer to native skin values than the control. (e) Quantification of hair follicles and sebaceous glands per area demonstrated that Fn wound dressings promoted recovery of skin appendage density close to the native state. This restoration was significantly higher than the control group for both hair follicles and sebaceous glands. Mean and standard error are shown. n = 5–8 wounds; **p < 0.01 vs. Healthy and #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01 vs. Fn in a one-way ANOVA on ranks with a post hoc multiple comparisons Dunn’s test. (f) To quantify the potency of our treatments, the different parameters measured in c-e were compared to native unwounded tissues and score from 0 to 100% match. Colored boxes are used to represent % match to healthy skin. (g) H&E sections at day 14 post-wounding reveals that wound contraction and hair follicle regeneration are acting synchronously. Wound contraction is observed by a significantly reduced wound size (from 8 mm to −2 mm, black arrowheads in inset), while hair follicle neogenesis is confirmed by the presence of hair follicle pegs growing from the new epidermis at the center of the wound.
