Figure 1.
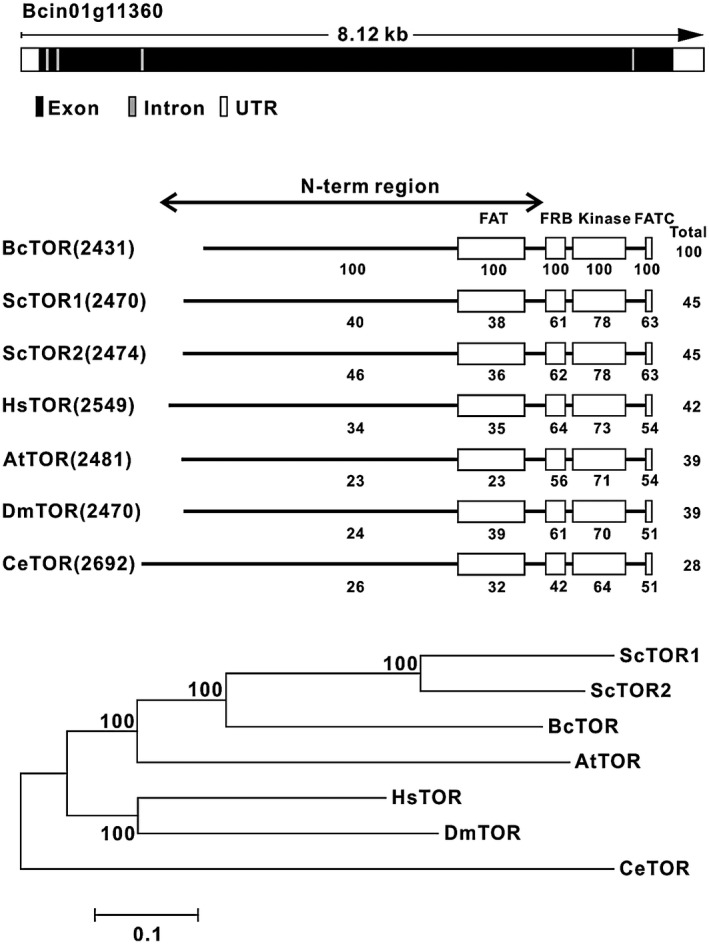
The information for the TOR homologue in Botrytis cinerea. (A) The gene locus and structure of the TOR homologue in B. cinerea. (B) Domain organization of BcTOR protein and comparison of the BcTOR amino acid sequence with those of TOR proteins from other organisms. (C) Phylogenetic analysis of BcTOR with that from other species. Bc, Botrytis cinerea; Sc, Saccharomyces cerevisiae; Hs, Homo sapiens; At, Arabidopsis thaliana; Dm, Drosophila melanogaster; Ce, Caenorhabditis elegans. Protein domain diagram shows number of HEAT (Huntingtin, elongation factor 3 (EF3), a subunit of protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A) and TOR1) repeats; FAT (FRAP, ATM and TRRAP) domain; FKP12‐rapamycin binding (FRB) domain; and carboxy‐terminal FAT (FATC) domain.
