Figure 3.
Bivalent Promoters Are Depleted in H3K4me3 in 2i Ground State
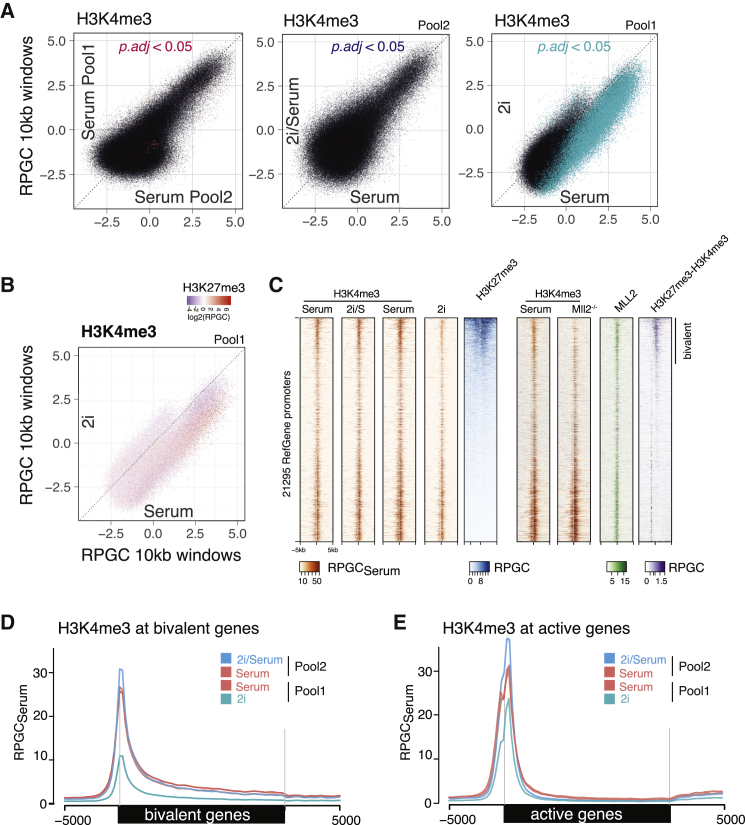
(A) Genome-wide analysis of H3K4me3 across 10-kb windows. H3K4me3 density (RPGCSerum) is plotted as log2-fold enrichment over input read density on x and y axis. Mean of three biological replicates is plotted and significance based on three biological replicates each (adjusted p value [p adj.] < 0.05) was tested using DESeq. (Left) H3K4me3 comparison between serum conditions in pool 1 and pool 2 is shown. Middle: comparison of 2i/serum and serum condition (pool 2) is shown. (Right) Comparison of 2i and serum condition (pool 1) is shown.
(B) Genome-wide analysis of H3K4me3 across 10-kb windows as in (A), comparing 2i and serum condition (pool 1) with color scale representing H3K27me3 levels in the same bin.
(C) Heatmap of all RefSeq transcription start sites. Plotted are densities (RPGCSerum) of H3K4me3 tracks from pool 1 and pool 2, as well as H3K27me3 in serum condition. Additionally, published Mll2 ChIP, H3K4me3 ChIP in Mll2−/−, and H3K4me3-H3K27me3 Re-ChIP are shown (Mas et al., 2018). Entire heatmap is sorted by H3K27me3 levels.
(D) Average quantitative profile of H3K4me3 across 1,969 bivalent genes, comparing 2i/serum and 2i conditions quantitatively to their respective serum control.
(E) Average quantitative profile of H3K4me3 across bivalent genes, comparing 2i/serum and 2i conditions quantitatively to their respective serum control. y axis shows reads per genomic content relative to serum condition (RPGCSerum), where serum conditions are scaled to 1× coverage.