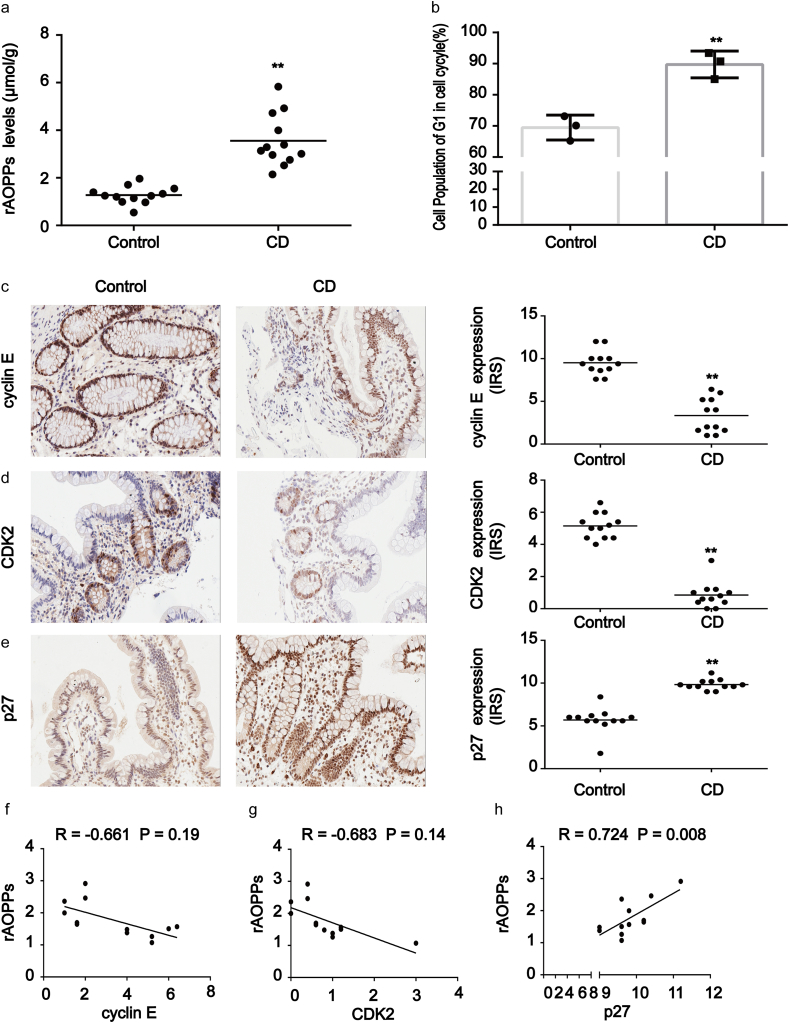
Fig. 1.
Accumulation of AOPPs in plasma correlated with cell cycle arrest in CD patients. (a) The relative plasma concentration of rAOPPs in controls (n = 12) and CD patients (n = 12). Plasma AOPPs were increased in CD patients compared to healthy subjects. (b) Bar graphs representing flow cytometry results showing G1 phase arrest in CD patients (n = 3) when compared with healthy controls (n = 3). (c–e) Images representative of immunohistochemical staining revealed the expression of cyclin E, CDK2 and p27kip1 in intestinal tissues from 12 healthy subjects and 12 CD patients. Scale bar, 20 μm. Data for the accompanying graphs were generated from immunoreactive scores (IRS). Overall, these results show a reduction of cyclin E (c) and CDK2 (d) with an induction in p27kip1 (e). Data are represented as IRS of cyclin E, CDK2 and p27kip1 in controls and CD patients. (f, g) Pearson correlation and linear analysis showing that the accumulation of AOPPs was negatively associated with cyclin E and CDK2 expression in tissues from CD patients (R = −0.661, P = 0.19; R = −0.683, P = 0.14). (h) Pearson correlation and linear analysis showing that the increased expression of p27kip1 was positively associated with AOPPs levels (R = 0.724, P = 0.008). **P < 0.01 versus controls. CD, Crohn's disease; rAOPPs, relative AOPPs.