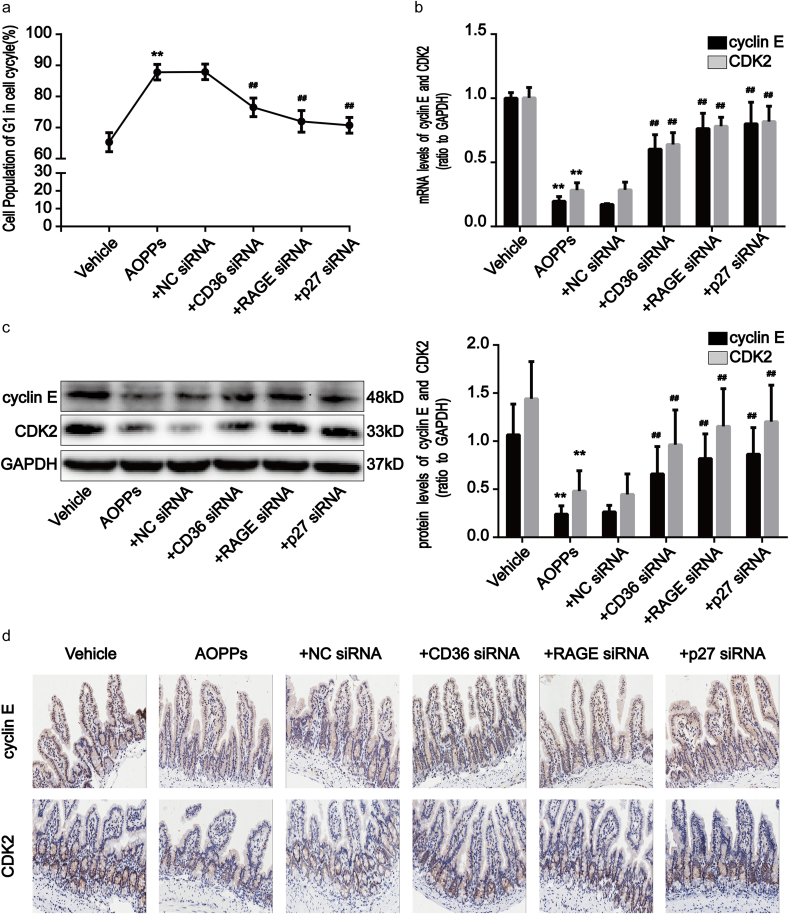
Fig. 8.
Acute AOPPs administration induced G1 phase arrest in C57BL/6 mouse IEC. (a) Primary intestinal epithelial cells were collected from mice after treatment with AOPPs for 5 days and analyzed by flow cytometry. The line chart indicates the percentage of G1 phase cells. Data revealed that AOPPs administration induced primary IEC G1 phase arrest compared with mice which were treated with a vehicle, and that treatment with AOPPs + CD36 siRNA, +RAGE siRNA and +p27kip1 siRNA attenuated G1 phase arrest in these cells. (b) Bar graphs representing qPCR analysis showing levels of cyclin E and CDK2 mRNA in mice with or without AOPPs treatment. (c) Representative Western blotting and densitometry quantification showing protein levels of cyclin E and CDK2 in mice with or without AOPPs treatment. Relative mRNA and protein levels were normalized with GAPDH, respectively. (d) Representative images of immunohistochemical staining for cyclin E and CDK2 in mice with or without AOPPs administration. Scale bars, 20 μm. Data are represented as mean ± SD, n = 5; error bars indicate SD. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01 versus the vehicle group; #P < 0.05 and ##P < 0.01 versus the AOPPs-treated group. Vehicle, PBS treatment.