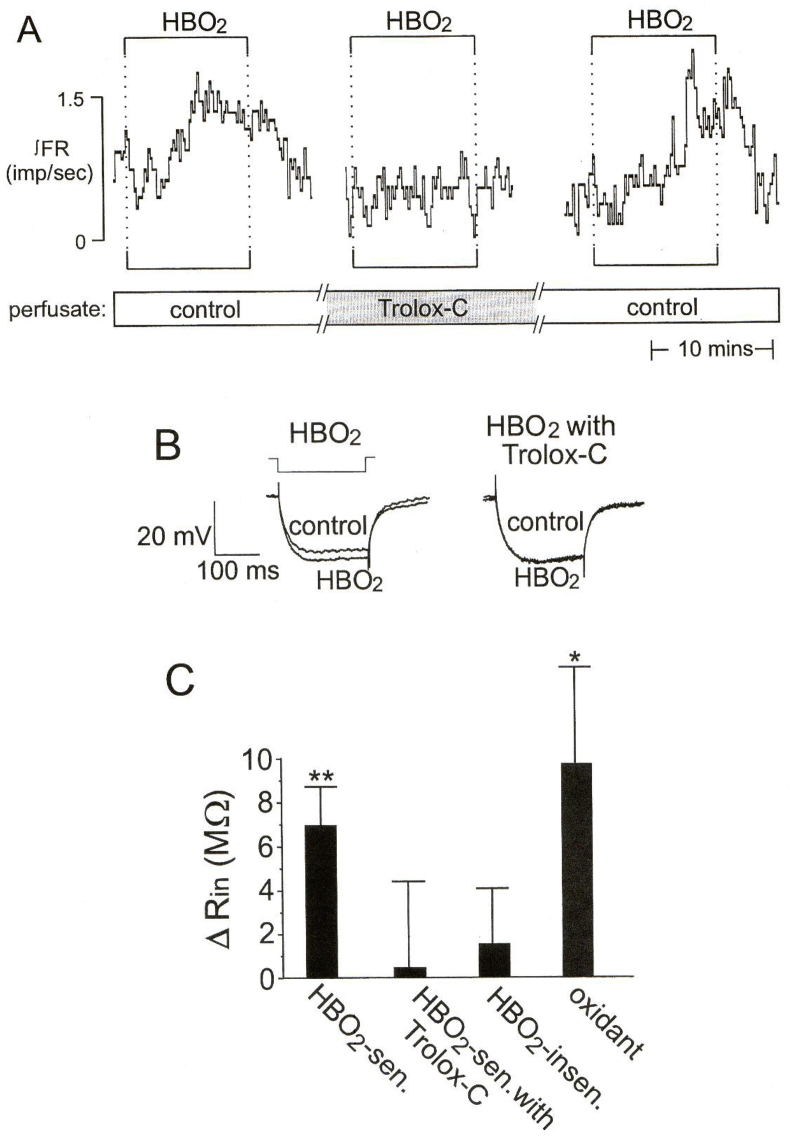
Fig. 2.
HBO2 increases input resistance, depolarizes membrane potential, and stimulates firing rate of neurons in the cSC in a rat brain slice. The excitatory effects of HBO2 are blocked by the antioxidant Trolox-C (100–200 μM), an analog of vitamin E. A) the trace of integrated firing rate (∫FR, impulses/s) measured via intracellular recording shows the ∫FR response to three bouts of HBO2 (3.3 ATA O2); control = 0.95 ATA O2 and PB = 3 ATA helium. An initial exposure to 3.3 ATA HBO2 increased ∫FR. After 90 min of incubation in medium containing the antioxidant Trolox-C, a second exposure to 3.3 ATA HBO2 did not affect ∫FR. Washing out Trolox-C for 30 min restored the excitatory ∫FR response to a third exposure to HBO2. B) average membrane potential (Vm) traces (n = 5) during −0.2 nA current injections show that the HBO2-induced increase in input resistance (Rin; where Rin α 1/membrane conductance) also was blocked by Trolox-C. C) bar graph showing average increase (Δ) in Rin (means ± SE) of HBO2-sensitive (n = 31), HBO2-sensitive plus Trolox C (n = 4), and HBO2-insensitive (n = 43) neurons. **Values significantly different from zero (t-test) at P < 0.001. Figure reproduced with permission from Journal of Applied Physiology, Mulkey et al. [140].