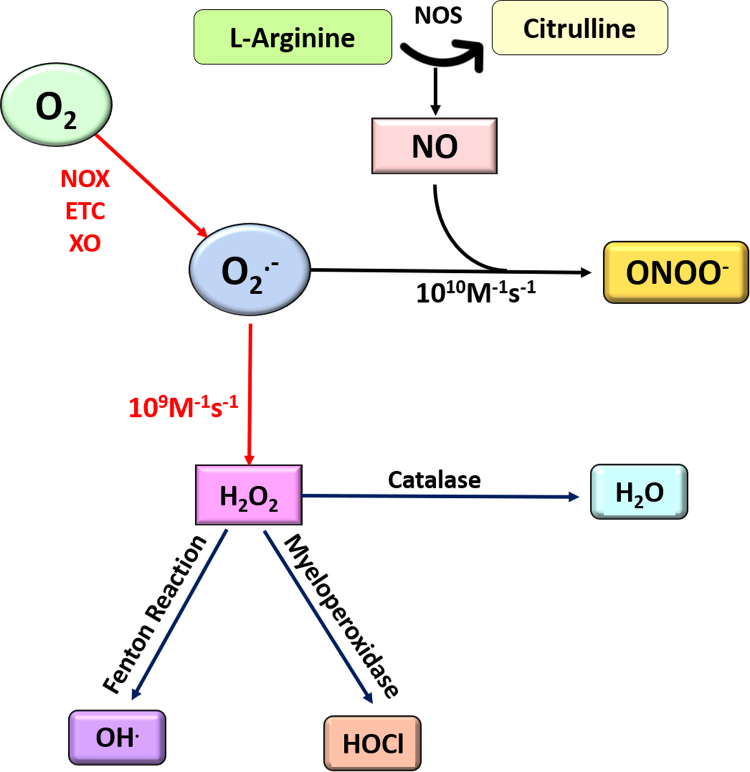
Fig. 3.
Reactive oxygen and nitrogen species: Superoxide anion is formed when molecular oxygen gains an electron and gets reduced. The source of electrons can be leakage from the mitochondrial electron transport chain (ETC), NADPH oxidase (NOX) or xanthine oxidase (XO). Superoxide is a short-lived ROS species that is instantaneously either dismutated to hydrogen peroxide through the activity of the enzyme SOD, or to RNS such as peroxynitrite through its reaction with nitric oxide. As is evident, there is a competition between formation of hydrogen peroxide and peroxynitrite in cells that is dictated by the balance between the activities of the two enzymes NOS and SOD. Hydrogen peroxide can further be fated to generate the highly reactive hydroxyl ions as a result of the Haber Weiss reaction in the presence of Ferrous ions or the biologically reactive hypochlorous acid. The activity of the antioxidant catalase on hydrogen peroxide on the other hand detoxifies it to generate water.