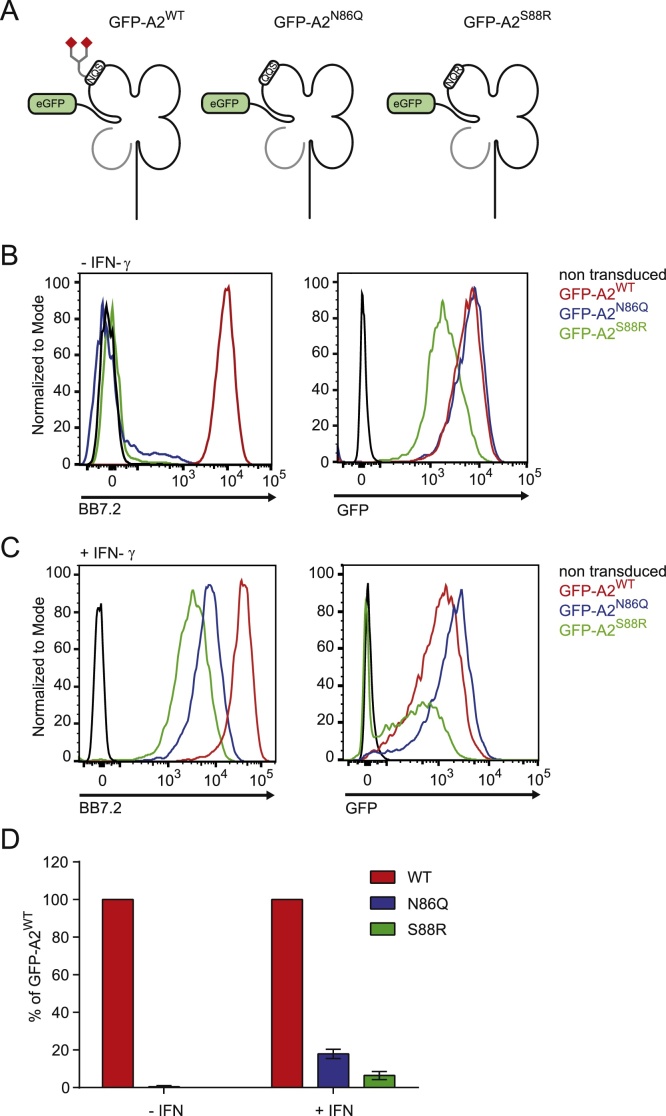
Fig. 1.
The N-linked glycan on MHC class I is required for efficient surface expression of GFP-A2. (A) Cartoon representation of the N-terminally GFP tagged HLA-A2 molecules used in this study. GFP-A2WT contains the consensus sequence that permits glycosylation of HLA-A2, whereas GFP-A2N86Q and GFP-A2S88R are non-glycosylated due to disruption of the motif. (B & C) Surface expression of GFP-A2 detected with the conformational specific mAb BB7.2 and total GFP expression to demonstrate transduction efficiency in HeLa-M cells expressing GFP-A2WT (red line), GFP-A2N86Q (blue line) and GFP-A2S88R (green line) in (B) the absence and (C) the presence of IFN-γ treatment for 48 h. Staining of non-transduced HeLa-M cell with BB7.2 is included as a control (black line).The results are representative of three independent experiments. (D) Bar graphs showing mean fluorescence intensity of surface HLA-A2 expression on the panel of GFP-A2 expressing cell lines as a percentage of GFP-A2WT. Error bars represent SEM from three independent experiments as performed in B & C. (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)