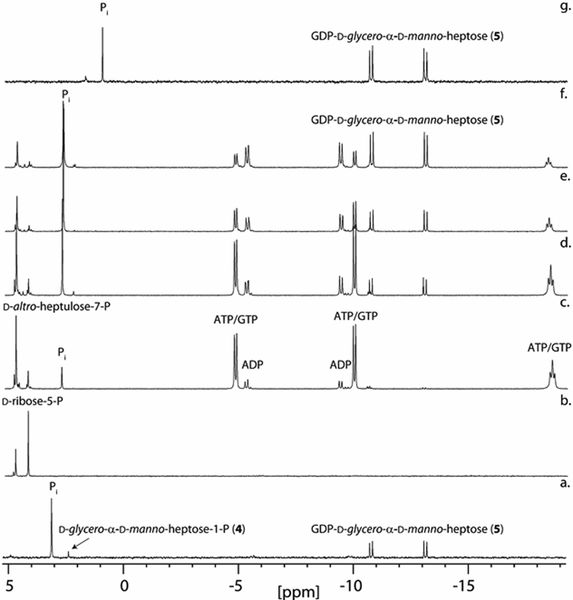
Figure 2.
31P NMR spectra for the time course of the preparative-scale biosynthesis of GDP-d-glycero-α-d-manno-heptose from d-ribose-5-P. (a) GDP-d-glycero-α-d-manno-heptose (5) after the addition of Cj1423, GTP, and pyrophosphatase to d-glycero-α-d-manno-heptose-1-P. (b) Spectrum of d-ribose-5-P with d-altro-heptulose-7-P added for reference. (c) 1 h after addition of all enzymes (TktA, Cj1423, Cj1424, Cj1425, GmhB, and pyrophosphatase) and co-factors as described in the text. (d) 6 h. (e) 24 h. (f) 48 h. (g) GDP-d-glycero-α-d-manno-heptose after rSAP degradation of remaining phosphate compounds (ATP/ADP, GDP, d-altro-heptulose-7-P) and anion-exchange column purification. The shift in the phosphate resonance is due to the change in pH after ammonium bicarbonate has been removed by acidification and then neutralized (final pH ~6).