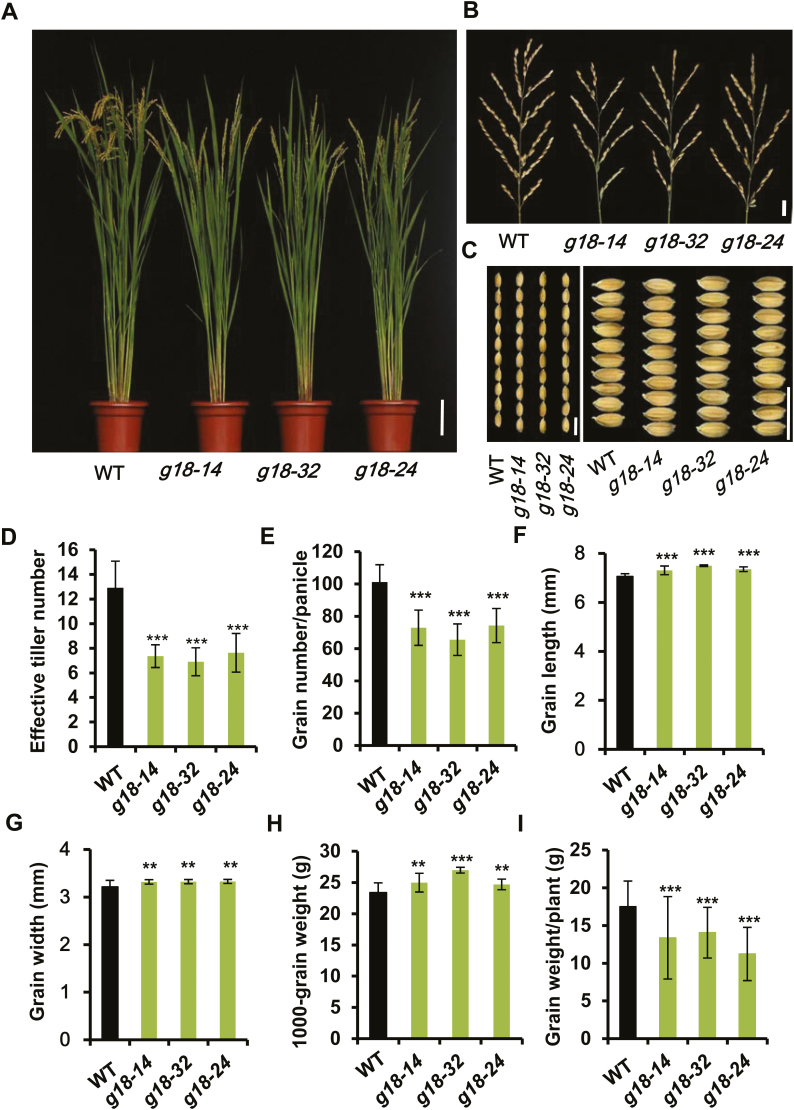
Fig. 6.
Mutation of osabcg18 affected multiple agronomic traits. (A) The phenotypes of osabcg18 mutant lines g18-14, g18-32, and g18-24 at the mature stage. Scale bar=10 cm. (B) Images of the panicles in the wild type and mutant lines in (A). Scale bar=2 cm. (C) Observation of the grain length (left) and width (right) in the wild type and mutant lines in (B). Scale bar=1 cm. (D) Effective tiller number in the wild type and mutant lines in (A). (E) The grain number per panicle in the wild type and mutant lines in (A). (F) The grain length and (G) width in the wild type and mutant lines. (H) The 1000-grain weight in the wild type and mutant lines. (I) The grain weight per plant in the wild type and mutant lines. Data are means ±SD (n=15); for the measurement of grain length and width, >150 seeds were measured for each plant. **P<0.01 and ***P<0.001 (Student’s t-test).