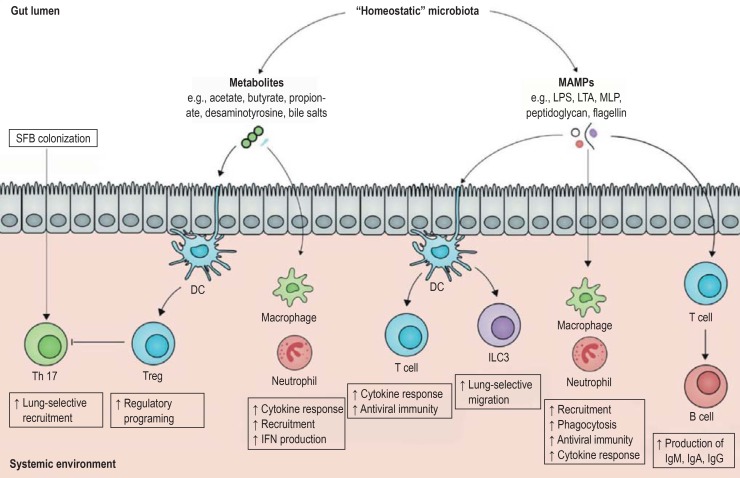
Figure 2.
The gut–immune axis (modified from [6]): metabolites synthesized by the human gut microbiota as well as bacterial surface markers play a crucial role in the regulation of the immune system via direct contact with immune system cells in the gut. DC, dendritic cell; Ig, immunoglobulin; ILC3, type-3 innate lymphoid cell; IFN, interferon; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; LTA, lipoteichoic acid; MAMP, microbe associated molecular pattern; MLP, murein lipoprotein; Treg, regulatory T cells; SFB, segmented filamentous bacteria; Th, T helper