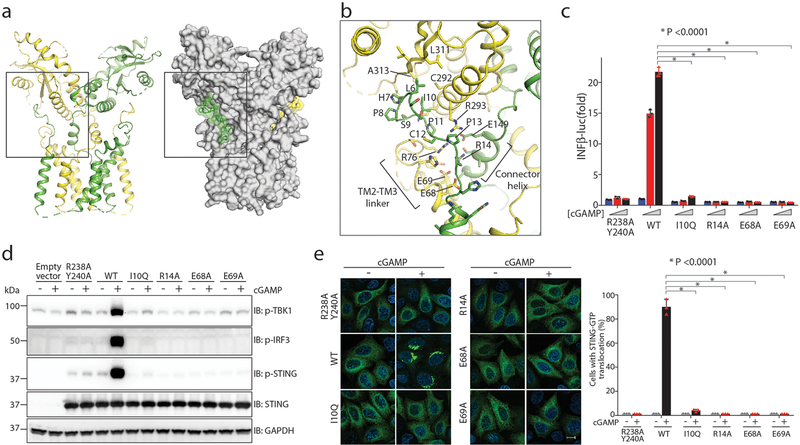
Fig. 2 |. Interaction between the N-terminal segment and the body of human STING.
a, Overview of STING N-terminal and body interaction in cartoon and surface representations. b, Detailed view of the interface. The view is expanded from the region in the box in a. c, Effects of STING mutation on the inter-domain interface in cGAMP-induced expression of the interferon-β 1 (IFNB1) gene. HEK293T cells that stably express IFNβ–luciferase reporter were transfected with expression vectors that encode wild-type (WT) or mutants of human STING. Cells were stimulated with three different concentrations of cGAMP (0, 0.3 and 1.4 μM). The R238A/Y240A mutant, which cannot bind cGAMP, was used as a negative control. Data are mean ± s.d. and representative of three biological replicates. d, Effects of STING mutations on the phosphorylation of STING, TBK1 and IRF3. HEK293T cells that express wild-type or mutant human STING were stimulated with cGAMP (1 μM) for 3 h and subjected to immunoblot analyses with indicated proteins. Data are representative of three biological replicates. e, Effects of STING mutations on the translocation and oligomerization of STING in cells. cGAS-deficient HeLa cells were transfected with expression vectors encoding wild-type or mutant STING–GFP. Representative confocal images with or without cGAMP stimulation are shown. Scale bar, 10 μm. The graph on the right is calculated from at least 150 cells. Data are mean ± s.d. and representative of three biological replicates.