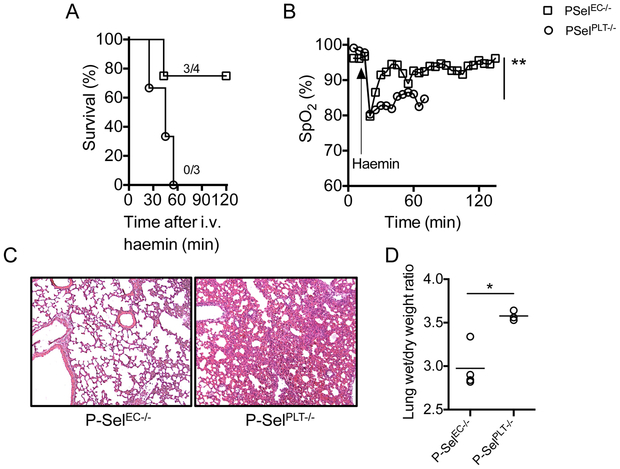
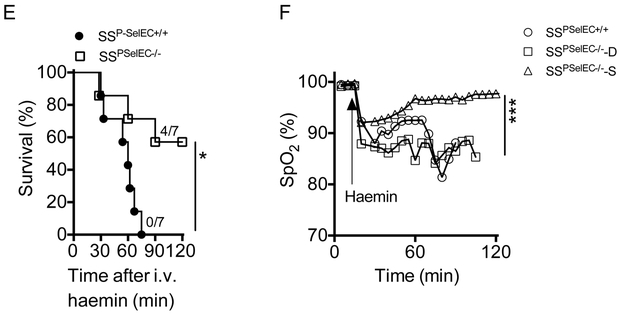
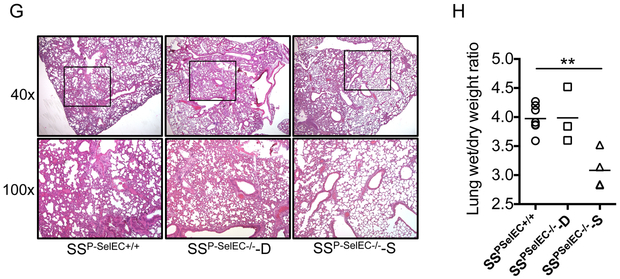
Figure 2. Expression of endothelial P-selectin mediates ACS in sickle mice.
(A) Mortality in B6 mice following haemin (210 μmol/kg) challenge in the presence (P-SelPLT−/−) or absence (P-SelEC−/−) of P-selectin on vascular endothelium. Haem induces (B) severe hypoxaemia, (C) lung damage and (D) pulmonary oedema in presence of endothelial P-selectin (P-SelPLT−/−) in B6 mice. (E) Survival of SSP-SelEC+/+ and SSP-SelEC−/− chimeric mice following infusion of haem (70 μmol/kg) (n=7; Mantel-Cox test; p<0.05). (F) Lung function, determined by SpO2 in SSP-SelEC+/+ mice, and SSP-SelEC−/− mice that died (SSP-SelEC−/− -D) or survived (SSP-SelEC−/− -S) following haem infusion (n=3; p<0.001). (G) Representative haematoxylin and eosin stained lung sections showing histopathology of lung following haem challenge in the indicated mice group. Note both SSP-SelEC+/+ and SSP-SelEC−/− -D mice had severe lung congestion (H) Gravimetric assessment of lung oedema (n = 3–6). Statistical analysis was performed using one-way ANOVA (*P < 0.01).