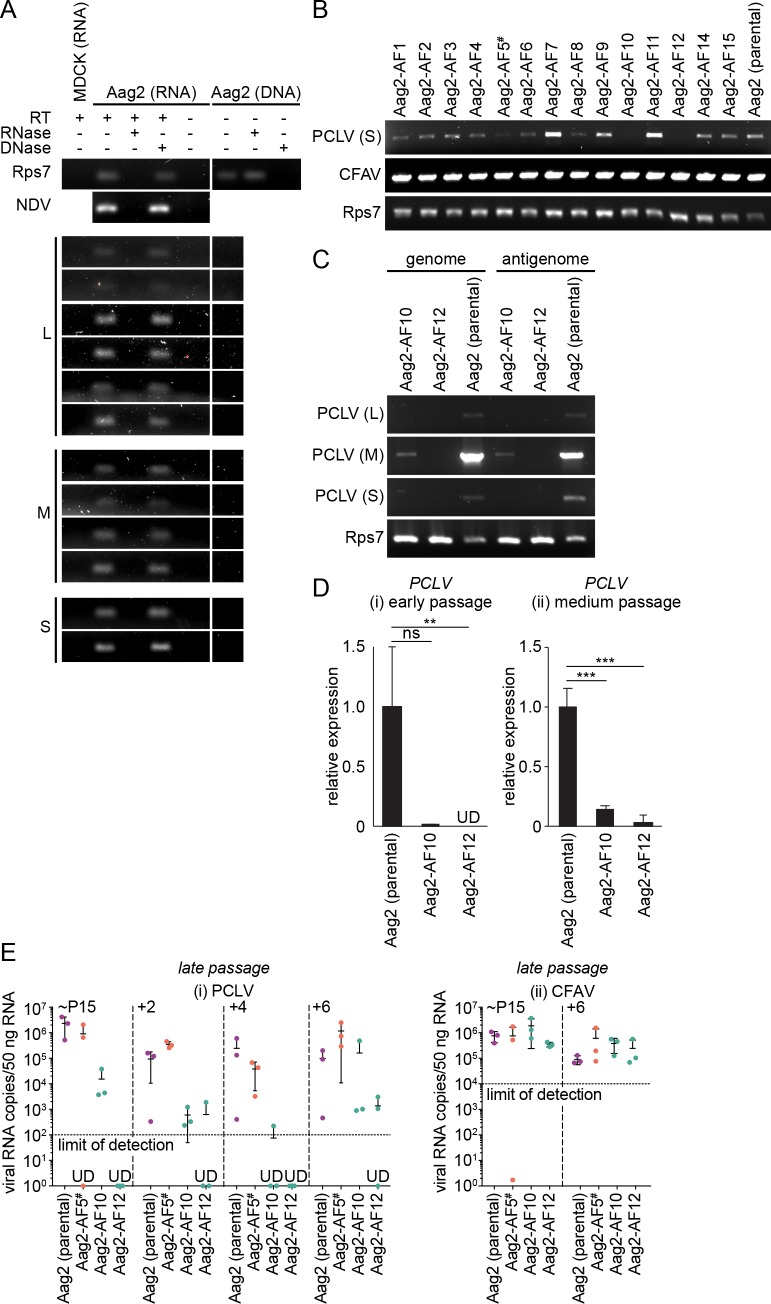
Fig 2. Aag2-AF10 and Aag2-AF12 cell lines harbour barely detectable levels of phasi charoen-like virus.
(A) Short PCR amplicons spanning the three PCLV genome segments (L, M, S) amplified from RNA or genomic DNA isolated from parental Aag2 cells, either with or without a reverse transcription step (RT). Purified nucleic acids were treated with RNase or DNase prior to PCR. MDCK cell RNA, the cellular Rps7 gene/mRNA and the RNA virus NDV, which was spiked into cells immediately prior to RNA extraction, serve as controls. (B) Detection of the PCLV S segment and CFAV by RT-PCR in Aag2-derived clonal cell lines. Cellular Rps7 mRNA serves as a loading control. (C) Detection of the PCLV L, M and S genome (-ssRNA) and antigenome (+ssRNA) segments in select Aag2-derived clonal cell lines by sense-specific RT-PCR. Rps7 mRNA serves as a loading control. (D) PCLV L segment RT-qPCR ΔΔCt (normalised to Rps7 mRNA) for select Aag2-derived clonal cell lines expressed relative to parental Aag2 cell line at (i) early passages (Aag2-AF10, passage 2; Aag2-AF12, passage 3) and (ii) later (‘medium’) passages (Aag2-AF10, passage 8; Aag2-AF12, passage 12). (E) RT-qPCR quantification of viral RNA copies for PCLV L segment (i) and CFAV (ii) at late passages in Aag2 (parental), Aag2-AF5, Aag2-AF10 and Aag2-AF10 cells. Starting passages (“~P15”) were passage 15 (parental Aag2), 12 (Aag2-AF5), 14 (Aag2-AF10) and 13 (Aag2-AF12). Data points represent three independently passaged lines. Error bars represent standard deviation. ** P < 0.01; *** P < 0.001; ns, not significant (one-tailed Student’s t test). UD, undetected. # Aag2-AF5 cell line used for CRISPR gene editing [60,61].