Table 5.
Per cent overall and per cent stratified by race/ethnicity of the reasons for breastfeeding cessation in a statewide sample of 323 Maryland WIC participants*
| Reasons for cessation | % | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total (n = 311) | African American (n = 114) | Hispanic (n = 63) | White (n = 134) | |
| Not enough milk | 23.4 | 19.5 a | 41.3 a , b | 18.4 b |
| Breast discomfort or pain | 16.9 | 23.0 c | 3.2 c , d | 18.4 d |
| Infant rejected breast | 14.1 | 11.5 e | 30.2 e , f | 8.8 f |
| Had to return to work | 12.8 | 19.5 g , h | 9.5 g | 8.8 h |
| Mother sick/taking meds | 9.3 | 8.0 | 4.8 | 12.5 |
| Other reasons † | 23.3 | 18.5 | 11 | 33.1 |
WIC, Special Supplemental Nutrition Program for Women, Infants, and Children. *Missing data on reasons for breastfeeding cessation on 12 participants.
†Other reasons include: infant sick (4.5%), infant seemed hungry (3.8%), infant irritable or not sleeping (1.0%), concerned about infant's growth (1.0%), to allow others to help (2.6%), others recommended (0.6%), infant seemed interested in other foods (2.2%), infant old enough for other liquids (2.6%), mother embarrassed (1.3%), mother smoked (1.0%) and others (3.2%).
aDifference by Hispanic vs. African American (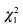 = 9.69, P = 0.003).
bDifference by Hispanic vs. white (
= 9.69, P = 0.003).
bDifference by Hispanic vs. white (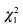 = 11.83, P = 0.001).
cDifference by Hispanic vs. African American (
= 11.83, P = 0.001).
cDifference by Hispanic vs. African American (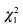 = 11.89, P < 0.001).
dDifference by Hispanic vs. white (
= 11.89, P < 0.001).
dDifference by Hispanic vs. white (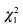 = 8.49, P = 0.003).
eDifference by Hispanic vs. African American (
= 8.49, P = 0.003).
eDifference by Hispanic vs. African American (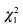 = 9.46, P = 0.003).
fDifference by Hispanic vs. white (
= 9.46, P = 0.003).
fDifference by Hispanic vs. white (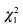 = 14.90, P < 0.001).
gDifference by Hispanic vs. African American (
= 14.90, P < 0.001).
gDifference by Hispanic vs. African American (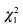 = 2.99, P = 0.09).
hDifference by African American vs. white (
= 2.99, P = 0.09).
hDifference by African American vs. white (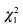 = 5.93, P = 0.02).
= 5.93, P = 0.02).
