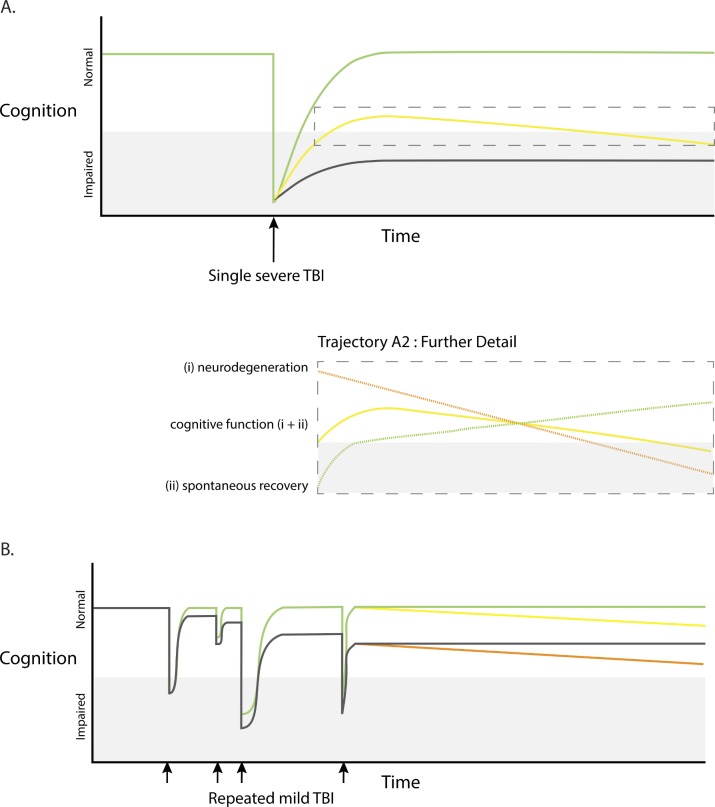
Figure 1.
Possible cognitive trajectories after traumatic brain injury (TBI). (A) Cognitive function in relation to single severe TBI (black arrow). Marked early deterioration in cognition which may recover fully (green colour), recover partially but subsequently deteriorate (progressive neurodegeneration, yellow colour), or recover partially leaving persistent non-progressive cognitive impairment (black colour). Further detail of trajectory A2 (dashed box) illustrating that overall cognitive function (yellow colour) may be influenced by a spontaneous recovery (green colour) and neurodegeneration (orange colour). (B) Cognitive function in relation to repeated mild TBI or ‘concussions’ (small black arrows). Possible trajectories include transient impairment in cognition associated with good recoveries and no progression (green colour), or late progressive neurodegeneration (yellow colour). TBI may be followed by incomplete recovery, without late progression (grey colour) or with late progressive deterioration (orange colour).