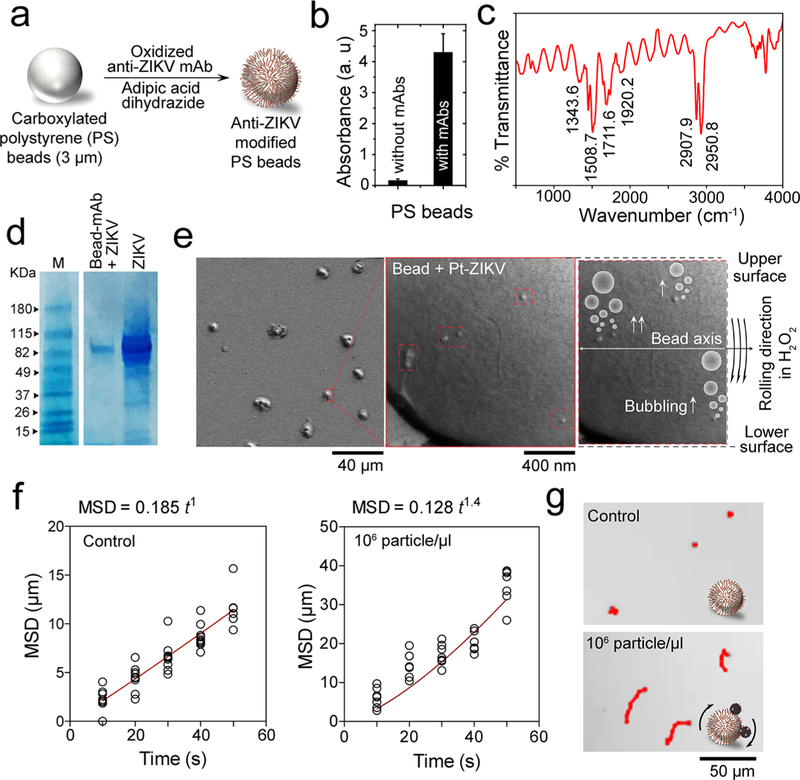
Figure 3.
Virus capture and induction of beads motion by Pt-nanomotors. (a) Schematic presentation of surface modification of PS beads with anti-ZIKV mAb. (b) UV–vis absorption values at 223 nm for beads with and without antibody modification. (c) FT-IR spectrum of the prepared anti-ZIKV mAb-modified beads, showing several peaks characteristics for protein at 1711.6, 1508.7, 1343.6, and 2907.9 cm−1. (d) SDS gel electrophoresis for ZIKV captured on the surface of antibody-modified beads. M: protein marker; Bead-mAb + ZIKV: virus captured on beads modified with anti-Zika mAb; ZIKV: Zika virus prepared in phosphate buffer saline at 105 particles/μL. (e) SEM analysis of beads with Pt-virus complexes. (f) Motion analysis of beads in the presence and absence of the target ZIKV tested under bright-field light microscopy using 200× magnification. (g) Representative images of motion trajectories of beads in the presence and absence of ZIKV under light microscopy.