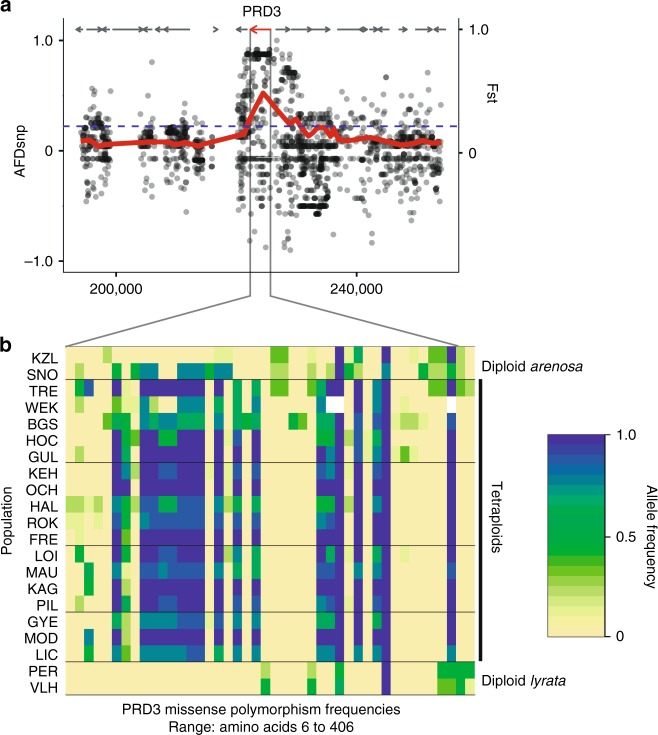
Fig. 2.
Selective sweeps and missense polymorphism frequencies by population. a Selective sweep example in PRD3, a gene involved in meiotic double strand break formation. X-axis gives chromosome 1 position in base pairs. Left Y-axis gives allele frequency differences between diploid and tetraploid A. lyrata and at single-nucleotide polymorphisms (dots). Right Y-axis (and red line) gives local Fst. Arrows indicate gene models. Red arrow indicates selective sweep candidate with localised differentiation. The dotted line gives the 99th percentile of genome-wide Fst values. b Zoom-in on PRD3 coding changes. Heatmap represents allele frequencies of missense polymorphisms. Frequencies 0–100% follow yellow to green, to blue. Derived diploid A. arenosa-specific missense polymorphisms are driven to high frequency in the tetraploids, whereas diploid A. lyrata alleles are absent, implicating diploid A. arenosa origin to this selected allele in the tetraploids