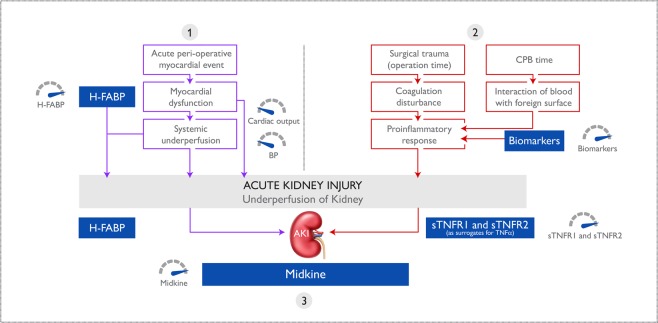
Figure 4.
Potential pathways involved in the pathogenesis of AKI. Three important pathways in the pathogenesis of AKI are represented by biomarkers in the model: (1) hypoperfusion (H-FABP), (2) proinflammation (sTNFR1 and sTNFR2 as surrogates for the transient TNFα response) and (3) ischaemia reperfusion injury (MK). Together with clinically measured variables, such as (among others) cardiac output and blood pressure (hypoperfusion and ischaemia reperfusion), cross clamp time and bypass time (proinflammation) biomarkers enable AKI patient risk categorisation. AKI, acute kidney injury; H-FABP, heart-type fatty acid-binding protein; sTNFR1, soluble tumour necrosis factor receptor 1; sTNFR2, soluble tumour necrosis factor receptor 2; TNFα, tumour necrosis factor alpha; MK, midkine.