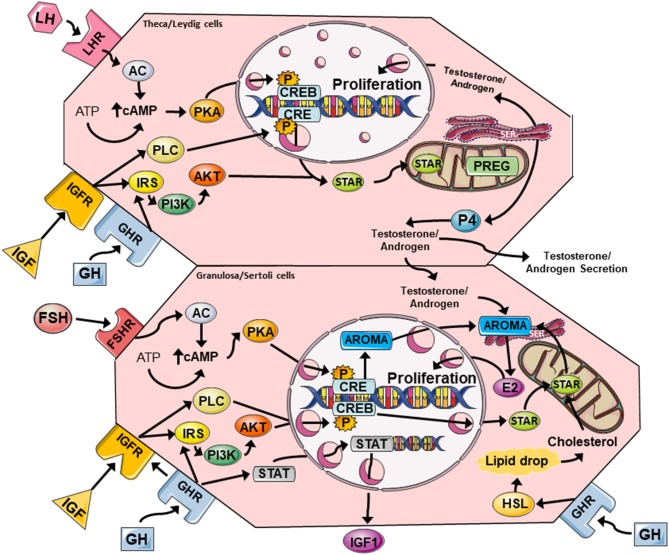
Figure 2.
A summary of the major GH and IGF signaling networks in female (theca/granulosa cell) and male (Leydig/Sertoli cell) reproductive physiology. Both GH and IGF can activate PLC/PKC and PI3K/Akt pathways that cross-talk with FSHR and LHR signaling via cAMP/PKA to promote steroidogenesis and cell proliferation. Steroidogenic events are mediated by CREB-dependent expression of aromatase (granulosa cells), and StAR expression in all cell types. StAR allows cholesterol to enter the mitochondria where it can be converted to PREG, and then subsequently to testosterone/androgens, estrogens, and progesterone. Estrogens and testosterone enhance cell proliferation via autocrine mechanisms, while GH can induce local IGF expression in granulosa and Sertoli cells via JAK/STAT signaling. LHR, luteinising hormone receptor; FSHR, follicle stimulating hormone receptor; AC, adenylate cyclase; cAMP cyclic AMP; PKA, protein kinase A; CRE, cAMP response element; CREB, cAMP response element binding protein; PLC, phospholipase C, IRS, insulin receptor substrate; PI3K/Akt, phosphoinositide 3-kinase/protein kinase B; StAR, steroidogenic acute regulatory protein; PREG, pregnenolone; SER, smooth endoplasmic reticulum; P4, progesterone; E2, estradiol; STAT, signal transducer and activator of transcription; AROMA, aromatase, HSL, hormone-sensitive lipase.