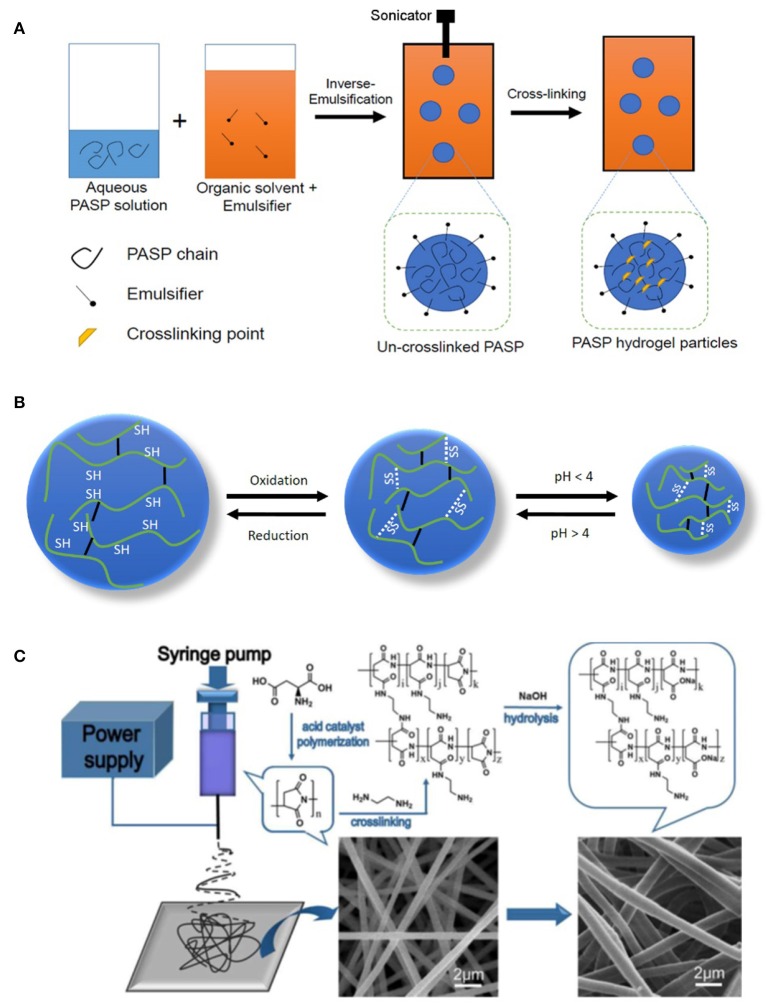
Figure 4.
Preparation of nanostructured PASP hydrogels. (A) Schematic representation of the preparation of PASP-based nanogels in inverse emulsion technique. (B) Schematic representing volume change of pH- and redox/reductive-responsive nanogels, white dashed lines represent cleavable disulfide bonds while solid black lines stand for permanent linker; oxidation leads to shrinkage of nanogels as crosslinking density increases, while acidic pH values protonate COOH groups of PASP, lowering the swelling. (C) Schematic representation of the method for PASP fiber hydrogel formation. Reproduced from Zhang et al. (2015) with permission from Elsevier.