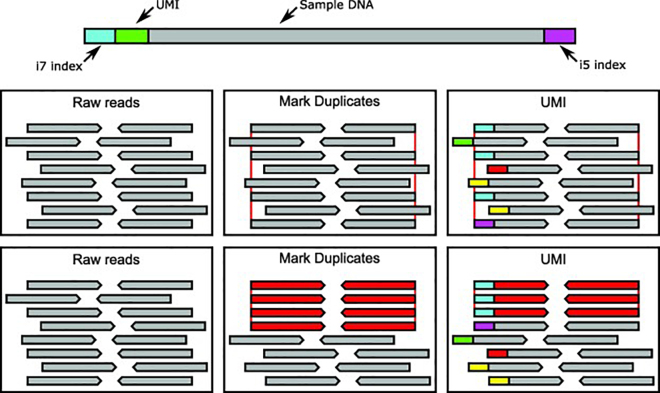
Fig. 3.
Considering duplicates in next generation sequencing. PCR duplicates can occur during the course of NGS. Whilst duplicates will appear to be separate reads, they are actually technical noise due to errors during PCR and sequencing. The two methods of correcting these errors are detailed above. The red lines indicate reads the start and end coordinates of the duplicates. Reads are coloured based on whether they are considered individual reads (grey) or duplicates (red), the coloured bars at the start of each read in the UMI panel represent different UMI sequences. In the above situation marking duplicates would cause 4 reads to be combined into a single read whereas the UMI based duplicate method is able to distinguish between true duplicates and unrelated reads with the same coordinates. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)