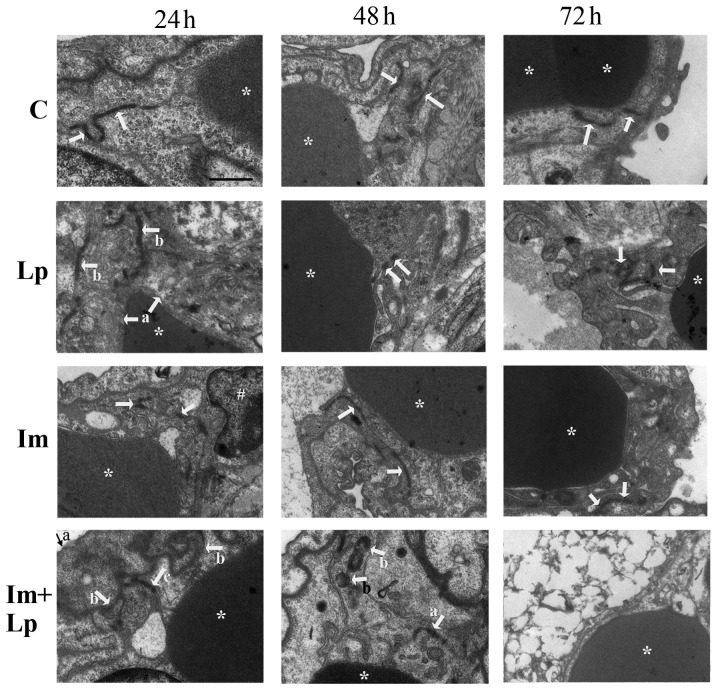
Figure 5.
Transmission electron microscopy images of pulmonary capillary endothelial cell junctions in lung tissues isolated from guinea pigs from the experimental groups. Pulmonary capillary endothelial cell junctions in the control group were normal (indicated by arrows). In the Lp-infected group, at 24 h, abnormal changes that could be observed included swollen vascular endothelial cells (indicated by arrows a) and partially opened cell junctions (indicated by arrows b); at 48 h, the endothelial cell junctions were completely opened (indicated by arrows); at 72 h, the cell junctions were obscure and partially opened (indicated by arrows). In the immunosuppressed group, at 24 h, the endothelial cell junctions were partially opened (indicated by arrows); at 48 h, the density of the cell junctions was reduced and the cell junctions were intermittently opened (indicated by arrows); at 72 h, the endothelial cell junctions had recovered to normal (indicated by arrows). In the immunosuppressed Lp-infected group, at 24 h, the alveolar epithelial cells were swollen (indicated by arrow a), the basement membrane was shrunken (indicated by arrows b), the density and number of cell junctions were reduced and the junctions were partially opened (indicated by arrow c); at 48 h, the number and densities of cell junctions were reduced and partially opened (indicated by arrow a), Lp bacteria were visible (indicated by arrows b); at 72 h, destruction of tissue structure was evident, the cell membrane was unclear, the nuclei were swollen, and the cell junctions had disappeared. *Denotes red blood cells and #denotes the nucleus. Scale-bars, 1 µm. C, control; Lp, Legionella pneumophila; Im, immunosuppressed.