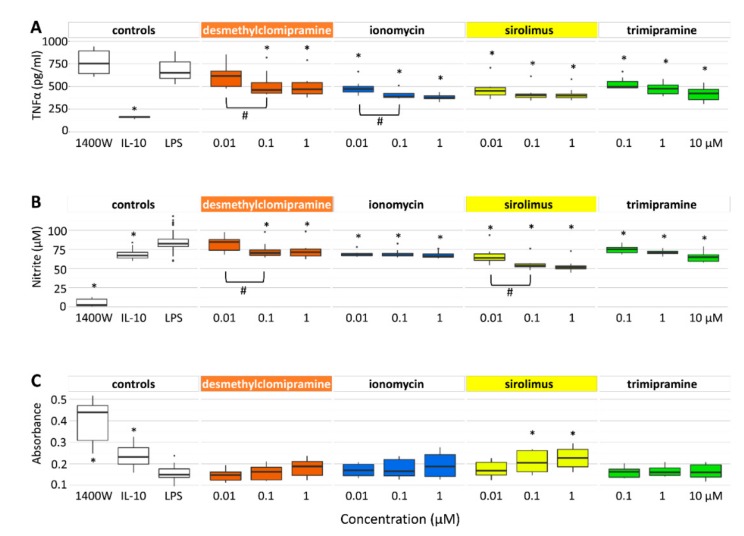
Figure 2.
In vitro validation of anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidant and neuroprotective effects of test compounds. (A) Treatment effect on neuroinflammation was assessed by measuring TNFα levels in the culture medium as a monitoring biomarker. All test compounds reduced TNFα and the effect was dose-dependent in the cases of desmethylclomipramine and ionomycin. (B) The treatment effect on nitric oxide –mediated neurotoxicity was assessed by measuring nitrite levels in the culture medium as a monitoring biomarker. All test compounds also reduced nitrite levels and the effect was dose-dependent in the cases of desmethylclomipramine and sirolimus. (C) The treatment effect on neuronal viability was assessed by measuring microtubule-associated protein 2-originated signals in the culture medium as a monitoring biomarker. Only sirolimus improved neuronal viability. Experiments were performed twice, each including quadruplicates of each test compound and concentration. Statistical significance: * p < 0.05 (as compared with non-treated control (LPS), Mann-Whitney’s u-test) and # p < 0.05 dose comparison (Mann-Whitney’s u-test). Abbreviations: lipopolysaccharide, (LPS); IL, interleukin; N-(3-(aminomethyl)benzyl)acetamidine, 1400 W (inducible nitric oxide synthase inhibitor).