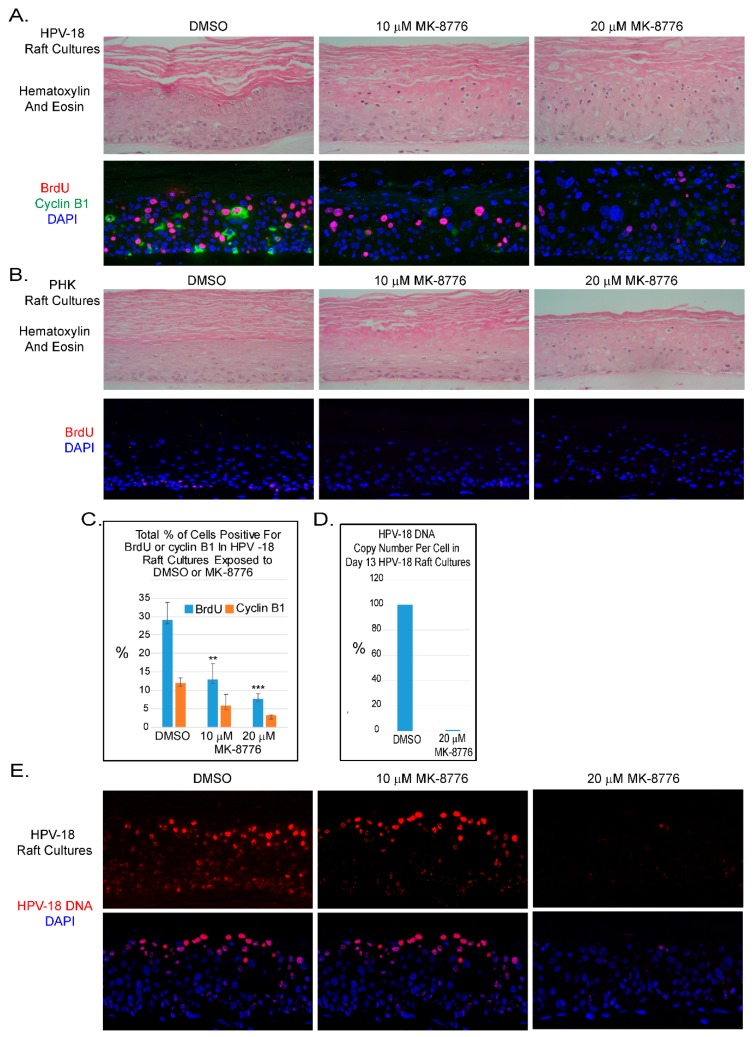
Figure 1.
Chk1 inhibitor, MK-8776, reduces host DNA replication and abrogates productive amplification of human papillomavirus (HPV)-18 in raft cultures. (A) Four micron tissue sections of HPV-18 raft cultures exposed to DMSO or 10 and 20 µM MK-8776 from days 7 to 12. Upper row, hematoxylin and eosin staining, showing cytotoxic effects, evident from condensed nuclei in upper differentiated strata. Cells were enlarged at the higher MK-8776 treated cultures. Lower row, dual immunofluorescence (IF) assay to detect BrdU incorporation (red) and cytoplasmic cyclin B1 accumulation (green). (B) Four micron tissue sections of uninfected PHK raft cultures exposed to DMSO or 10 and 20 µM MK-8776 from days 7 to 12. Upper row, H&E staining. Cytotoxicity was much less pronounced than the HPV-18 raft cultures. Lower row, indirect immunofluorescence assay of BrdU incorporation (red) revealed host DNA replication in the basal layer was abrogated by MK-8776 exposures. (C) Bar-graphs of percentages of BrdU (blue) and Cyclin B1 (orange) positive cells in DMSO and MK-8776 treated (days 7–12) HPV-18 infected raft cultures. The data were collected from three non-overlapping microscopic fields from the same experiment. Statistical analyses were performed by using Microsoft excel to determine significance of difference (p values) indicated as ** (p < 0.05) or *** (p ≤ 0.005). (D) Bar-graph showing percentage of HPV-18 DNA copy number per cell in control and MK-8776 treated (days 7–13) raft cultures, as determined by quantitative real time PCR. (E) Upper row, detection of HPV-18 DNA amplification in raft culture tissue sections by FISH (fluorescent in situ hybridization). Bottom row, merged images with DAPI (blue)-stained nuclei. Nuclei were also detected with DAPI in A and B panels. Images were captured with 20× objective magnification.