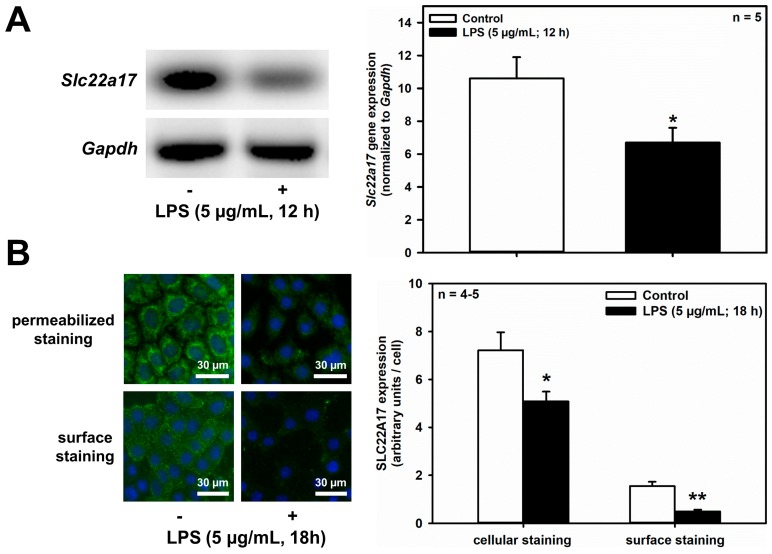
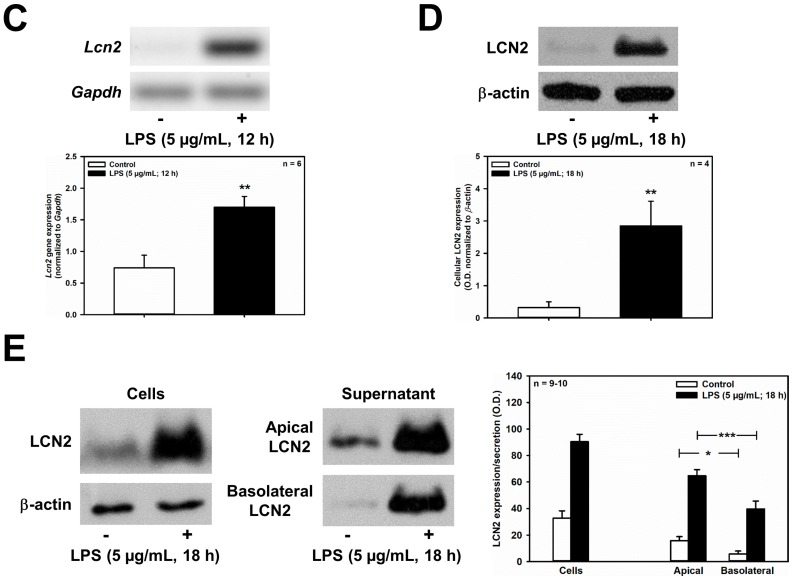
Figure 5.
LPS decreases Slc22a17/SLC22A17 expression and increases Lcn2/LCN2 expression in mCCD(cl.1) cells. (A) Expression levels of Slc22a17 mRNA by RT-PCR, in mCCD(cl.1) cells treated with 5 μg/mL lipopolysaccharides (LPS) for 12 h. Slc22a17 mRNA expression was normalized to Gapdh. Data show means ± SEM of five experiments. Statistical analysis compares the effects of control versus LPS by unpaired t-test. (B) Expression of SLC22A17 in mCCD(cl.1) cells treated with 5 μg/mL LPS for 18 h was detected by immunofluorescence microscopy of permeabilized and non-permeabilized (“surface staining”) cells, using a SLC22A17 antibody directed against the extracellular N-terminus. Hoechst 33342 counterstains nuclei. Statistical analysis shows means ± SEM of 4–5 experiments and comparison of the two conditions by unpaired t-test. (C) Expression levels of Lcn2 mRNA by RT-PCR in mCCD(cl.1) cells treated with LPS. Lcn2 mRNA expression was normalized to Gapdh. Data show means ± SEM of six experiments. Statistical analysis compares the effects of control versus LPS by unpaired t-test. (D) Effect of LPS on expression of LCN2 protein in mCCD(cl.1) cells. Cellular LCN2 protein expression was normalized to β-actin. Data show means ± SEM of four experiments. Statistical analysis determines the effect of LPS on cellular LCN2 protein using unpaired t-test. (E) Effect of LPS on cellular expression and secretion of LCN2 protein in mCCD(cl.1) cell monolayers, grown to confluence on transwell filters. LPS or solvent were applied to both apical and basolateral chambers for 18 h. Cells were lysed, apical and basolateral media were collected and concentrated to the same volume, as described in the Methods. Corresponding corrected volumes of concentrated media were loaded for immunoblotting. Data show cellular LCN2 protein expression normalized to β-actin, as means ± SEM of 9–10 experiments. Statistical analysis determines the effect of LPS on cellular and apically or basolaterally secreted LCN2 protein, using one-way ANOVA. For a definition of asterisks, see “statistics” in the Methods.