Figure 1.
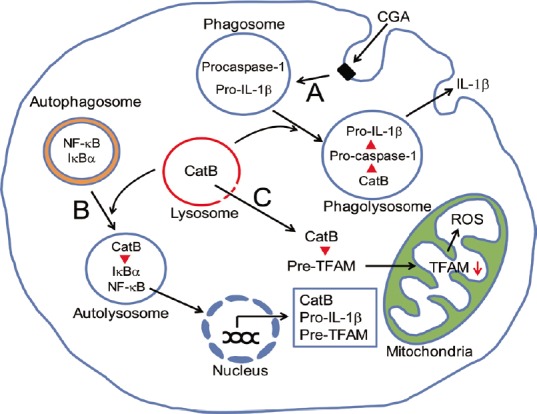
Schematic illustration representing critical roles of microglial cathepsin B (CatB) in chronic inflammatory and oxidative responses.
(A) CatB-dependent phagosomal pathway for proteolytic processing and secretion of interleulin (IL)-1β through proteolytic activation of procaspase-1. (B) CatB-dependent autophagic pathway for chronic nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) activation through proteolytic degradation of NF-κB inhibitor α (IκBα). (C) CatB leakage-dependent pathway for increased mitochondria-derived ROS generation through proteolytic degradation of pre-TFAM in the cytosol. CGA: Chromogranin A; ROS: reactive oxygen species; TFAM: mitochondrial transcription factor A.
