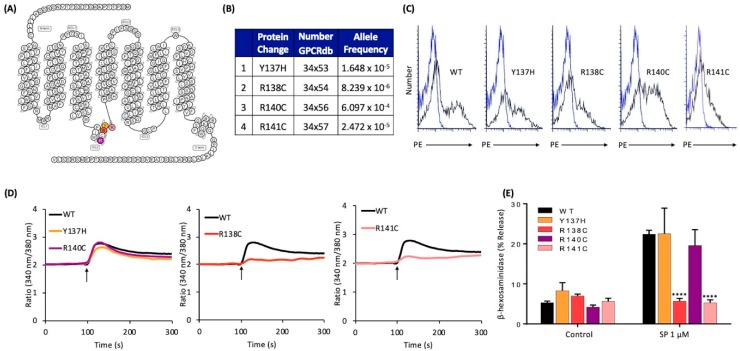
Figure 4.
Effects of naturally occurring MRGPRX2 variants at the receptor’s intracellular loops (Y137H, R138C, R140C, and R141C) on SP-induced responses in transiently transfected RBL-2H3 cells. (A) Snake diagram of secondary structure of MRGPRX2. Each circle represents amino acid residue with one letter code. Solid yellow, red, purple, and pink backgrounds denote the naturally occurring MRGPRX2 variants; (B) amino acid change for each MRGPRX2 variant with allele frequency; (C) cell surface expression of WT-MRGPRX2 and its variants was determined by flow cytometry using PE-anti MRGPRX2 antibody. Representative histograms for WT/variant (black line) and control untransfected cells (blue line) are shown; (D) cells expressing WT-MRGPRX2 and its variants were loaded with Fura-2 and intracellular Ca2+ mobilization in response to SP (1 μM) was determined. Data shown are representative of three independent experiments; (E) cells were exposed to a buffer (control) or SP (1 μM) for 30 min, and β-hexosaminidase release was determined. All data points are the mean ± SEM of at least three experiments performed in triplicate. Statistical significance was determined by a nonparametric t-test. **** p ≤ 0.0001.