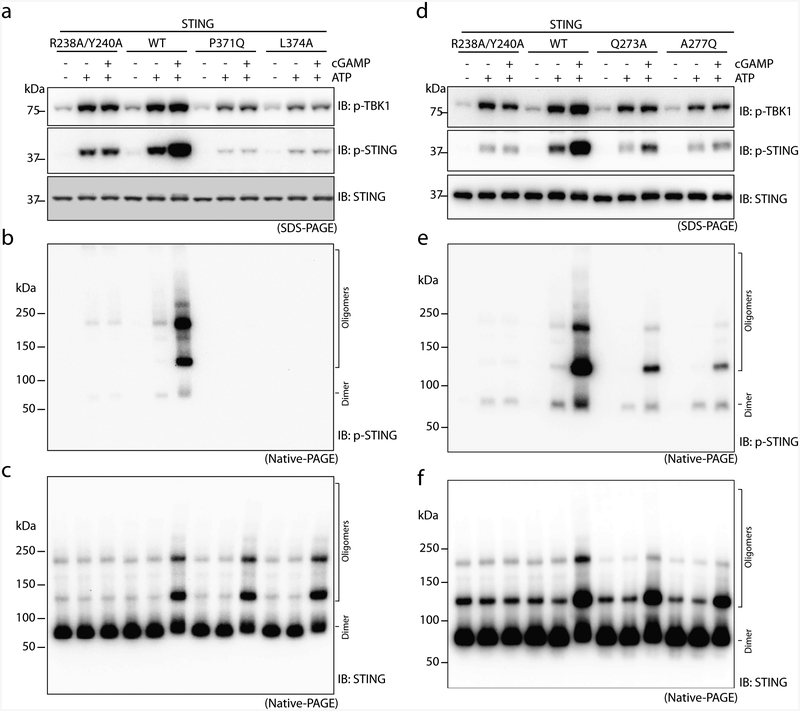
Extended Data Fig. 6 |. The binding and phosphorylation of STING by TBK1 relies on the interface between TBK1 and the STING C-terminal tail, and on the oligomerization of STING.
a, Mutations of TBK1-binding residues in the STING tail diminish cGAMP-induced phosphorylation of both TBK1 and STING. The S1 post-nuclear supernatant from HEK293T cells that express either the STING wild type or mutants was incubated with ATP in the presence or absence of cGAMP, and subjected to immunoblotting analyses for pTBK1, pSTING and STING. b, c, Mutations of TBK1-binding residues in the STING tail diminish cGAMP-induced STING phosphorylation (b) but not STING oligomerization (c). The same samples as in a were resolved by native gels, and analysed by immunoblotting. d–f, Mutations at the oligomerization interface of STING reduce cGAMP-induced oligomerization of STING, as well as phosphorylation of TBK1 and STING. The mutants are based on the accompanying paper on the structures of full-length STING12. The analyses in d, e and f were conducted in the same manner as in a, b and c, respectively. Data shown here are representative of at least three independent biological replicates.