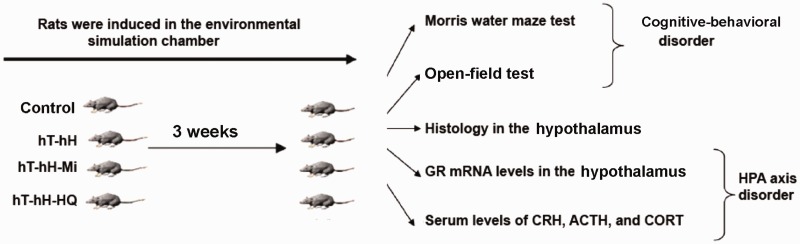
Figure 1.
Research scheme for stress induction and evaluation of cognitive–behavioral phenotypes and disorders in the HPA axis in rats exposed to hT and hH. Forty SD rats were randomly assigned to four groups: control group; hT-hH group (35 ± 1°C and 85 ± 5% humidity); hT-hH-Mi group (35 ± 1°C and 85 ± 5% humidity and 25 mg/kg mifepristone daily), and hT-hH-HQ group (35 ± 1°C and 85 ± 5% humidity and 1 mL/100 g HQ decoction daily). Control rats and stress-induced rats were subjected to the Morris water maze test, open-field test, pathologic analysis, and assays for detecting the expression of GR mRNA in the hypothalami and serum levels of CRH, CORT, and ACTH 3 weeks after treatment (N = 10 for each group). ACTH, adrenocorticotropic hormone; CORT, corticosteroid; CRH, corticotropin-releasing hormone; GR, glucocorticoid receptor; Mi, mifepristone; hH, high-humidity; HPA, hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal; HQ, Huang Qin Hua Shi; hT, high-temperature.