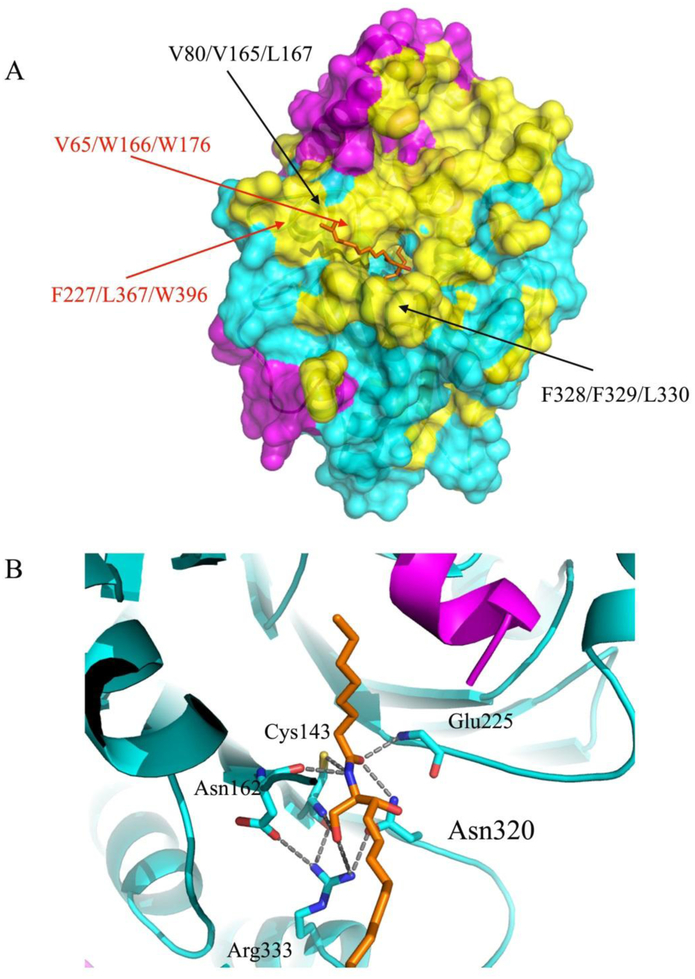
Figure 3. Hydrophobic surface of AC with a modeled ceramide substrate.
(A) The surface representation of the hydrophobic areas of the AC in ribbon diagram are colored yellow and the remaining residues are colored in magenta (α-subunit) and in cyan (β-subunit). The locations of the residues mutated in our previous work (black) and that of the residues forming plausible hydrophobic contacts with the substrate d17 moiety (red) are labeled30. (B) Close-up view of the modeled C8 ceramide substrate (d17:1/8:0, ball and stick in orange) interacting with enzyme residues in the substrate-binding area. The positions of several AC catalytic residues, which can form hypothetical interactions with the substrate in the tetrahedral complex, are indicated.