Figure 4. HVEM behaves as bidirectional switch based on environmental signals:
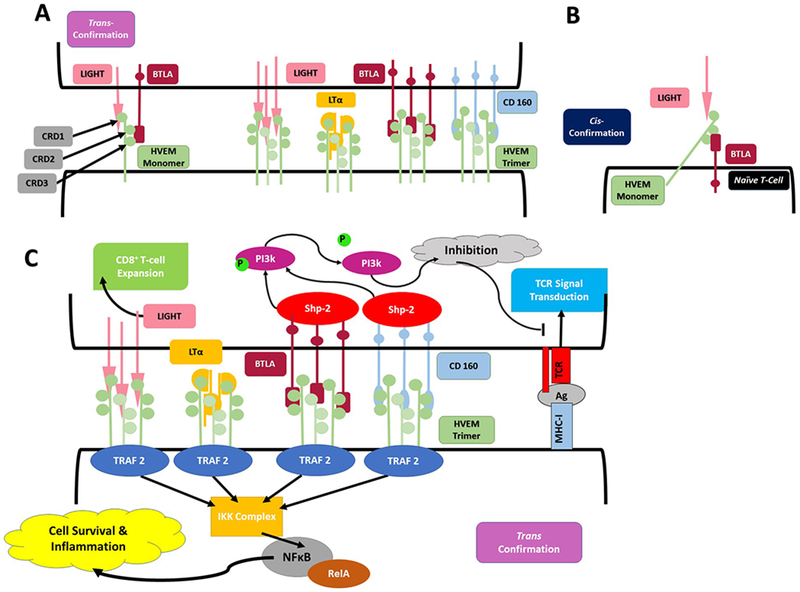
A. HVEM associates with LIGHT, LTα, BTLA, and CD160 in trimeric confirmations when expressed in trans confirmation. LIGHT and LTα associated with CRD1 binding domain, while BTLA and CD160 associate with CRD2/3. All ligands associate with HVEM in a trimeric confirmation, generating a 3:3:3 complex of 3 HVEM molecules with 3 BTLA or CD160 molecules and 3 LIGHT or LTα molecules. B. HVEM interacts with coexpressed BTLA to from an inert complex when both are expressed in their cis confirmation, most commonly on naÏve T-cells. In this formation HVEM can still associate with soluble LIGHT or LTα at its exposed CRD1 binding domain, yet no downstream signal is generated from the interaction. C. When HVEM is expressed in the trans confirmation on the membrane, ligation of LIGHT, LTα, BTLA or CD160 results in TRAF2 recruitment within the HVEM expressing cell. TRAF2 activates an IKK complex which in turn activates the RelA form of NFκB to promote cell survival. Within BTLA and CD160 expressing cells, ligation of HVEM results ITIM phosphorylation, recruiting SHP1 and SHP2, ultimately resulting in inhibitory signaling interrupting TCR signal transduction via dephosphorylation of PI3k -PKB pathway. Despite apparent absence of intracellular signaling motifs, LIGHT ligation of HVEM stimulates CD8+ T-cell expansion.
