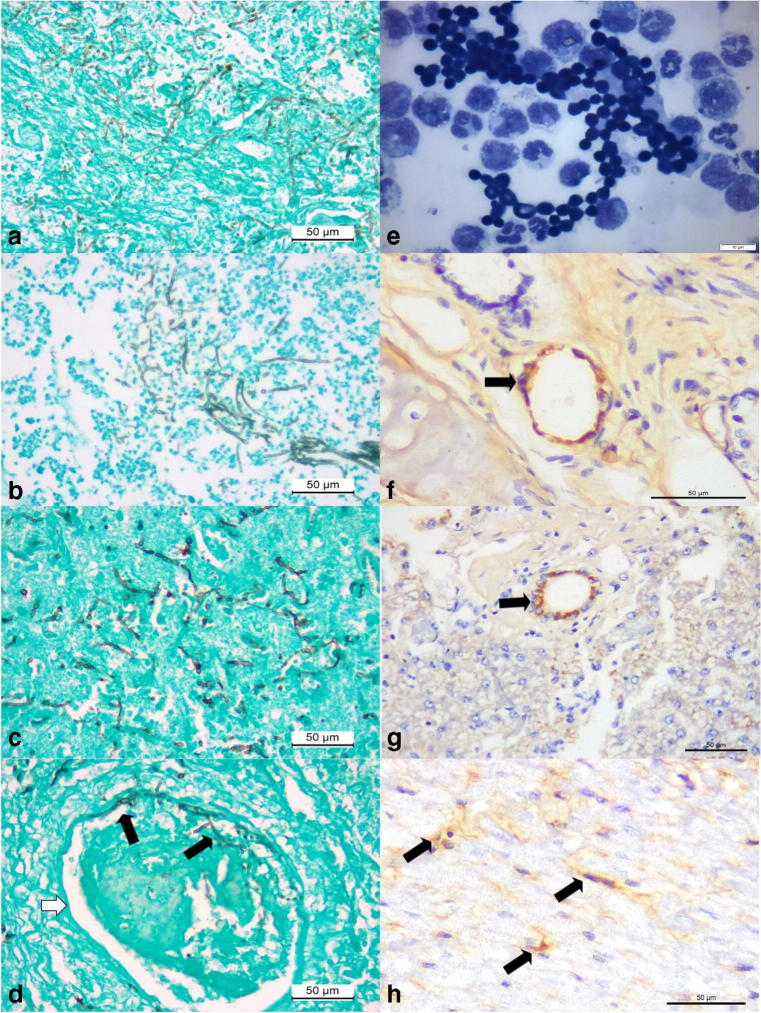
Fig. 4.
Histochemical, cytological, and immunohistochemical findings of disseminated phaeohyphomycosis in a dog with simultaneous infections by canine adenovirus-1 (CAdV-1) and canine parvovirus-2 (CPV-2). Observe intralesional accumulations of septate fungal hyphae in the liver (a), kidney (b), and the cerebral cortex (c). There is vascular invasion of septate hyphae (black arrows) within the damaged vein (white arrow) of the cerebral cortex (d). Cytological evaluation of the cerebrospinal fluid revealing elevated number of fungal organisms (e). Immunohistochemical identification of antigens of CAdV-1 (arrows) within epithelial cells of mixed glands of the lungs (f) and epithelial cells of bile ducts within the liver (g). There is positive immunolabeling for antigens of CPV-2 (arrows) within degenerated cardiomyocytes of the myocardium (h). Gomori methenamine-silver histochemical stain, a–d; panoptic stain, e; immunoperoxidase counterstained with hematoxylin, f–h. Bar, a–d, f–h, 50 μm; e, 10 μm