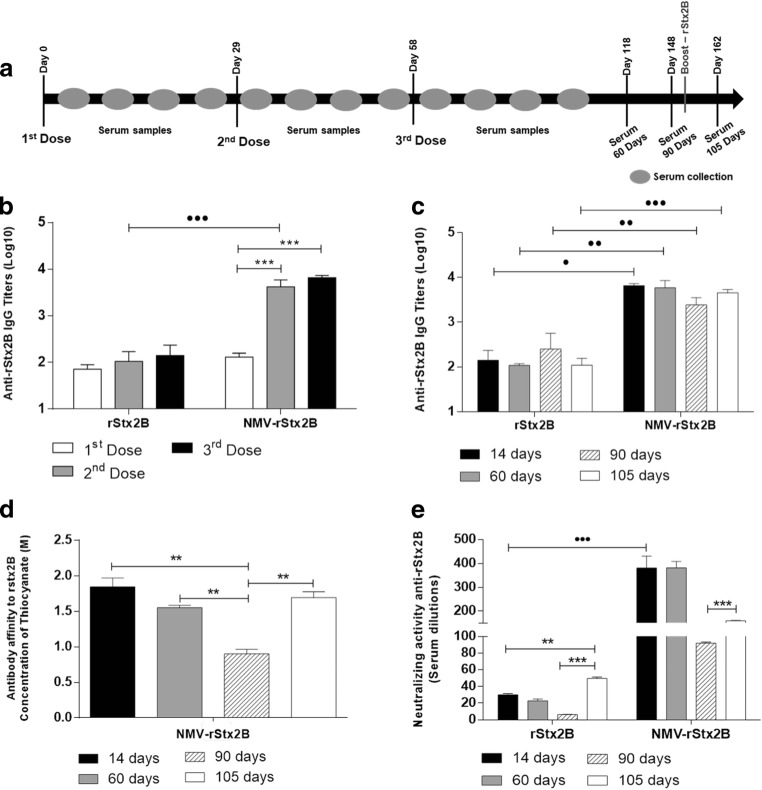
Fig. 3.
NMV-rStx2B vaccine formulation improves magnitude and quality of the Stx2-specifi humoral immune response. Female BALB/c mice (n = 5/group) were subcutaneously immunized with three doses of rStx2B or NMV-rStx2B. Ninety-one days after the last dose, the animals were inoculated with a 25-μg dose of the rStx2B protein, except for the control group (NMV). Sera were collected on days 7, 14, 21, and 28 after each dose and at 60, 90, and 105 days after the last dose and analyzed by ELISA assay (as described in the Methodology section), and the anti-rstx2 titers were measured. a Schematic representation of the vaccination protocol. b, c Evaluation of anti-rStx2B IgG response from sera harvested 14 days after each vaccine dose (b) or 60, 90, and 105 days after the last dose (c). The antibody titers were determined by ELISA and the values obtained for the control group (NMV) were subtracted from the titers determined for the experimental groups (MEAN + 2 × SD). d Antibody affinity of the sera collected at different days after the third dose. Bars represent the molar concentrations of ammonium thiocyanate required to dissociate 50% of the antibodies bound to Stx2B. e Stx2 Neutralizing activity of the anti-Stx2B antibodies against the Stx2-induced cytotoxic effects in cell culture. The maximum dilution required to preserve 50% of the viable cells were determined for each serum sample. The data correspond to the mean values ± SE of the individual values for each group in duplicate. Statistical differences are indicated by brackets: ***p < 0.001, **p < 0.01, *p < 0.05, for one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post-test for the analysis as a function of the day each dose inoculation •••p < 0.001, ••p < 0.01, •p < 0.05 (t test) for the intergroup analysis