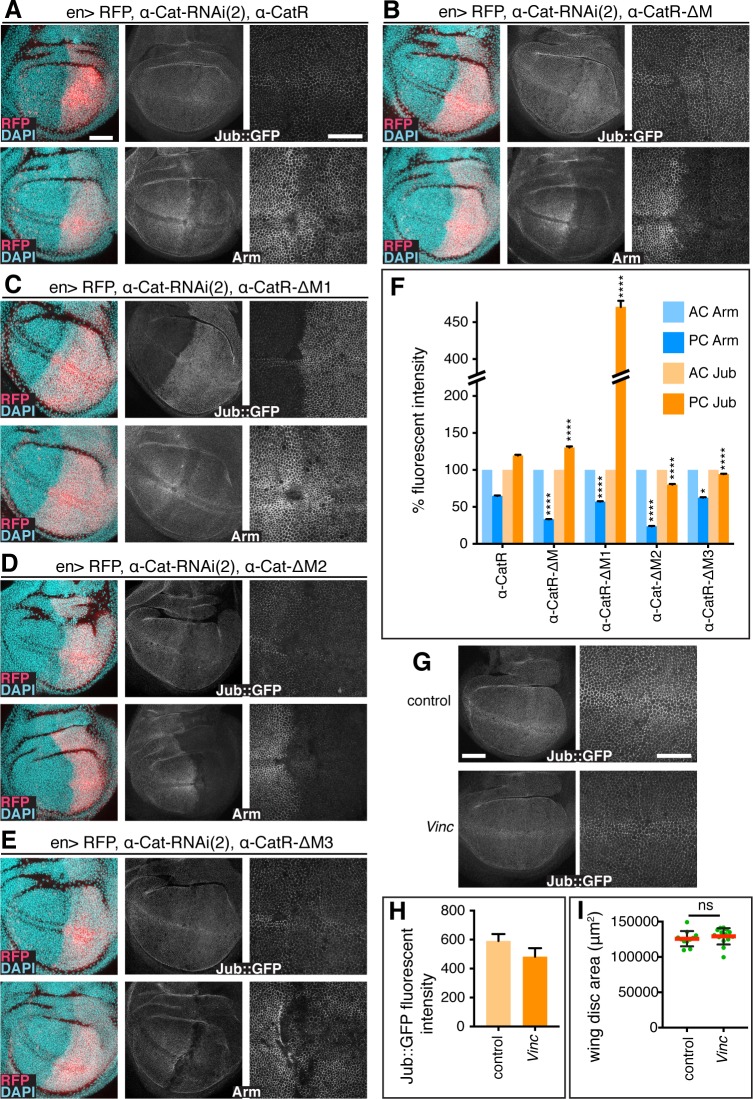
Fig 7. The M1 domain of α-Cat limits recruitment of Jub to AJs.
(A-E) Late 3rd larval instar discs expressing en-Gal4, UAS-RFP, UAS-α-Cat-RNAi(2) and either UAS-α-CatR (A), UAS-α-Cat-ΔM (B), UAS-α-CatR-ΔM1 (C), UAS-α-Cat-ΔM2 (D), or UAS-α-CatR-ΔM3 (E). Discs express Jub::GFP controlled by its endogenous promoter (upper panels) and are stained for Arm (lower panels). Nuclei are labeled with DAPI. Close-up images to the right show wing pouch area on both sides of the anterior-posterior compartment boundary. Scale bars, 50 μm and 25 μm. (F) Comparison of relative fluorescent intensities between anterior compartment (AC) and posterior compartment (PC) for Jub::GFP (N = 500–1000 cells from five wing discs) and Arm (N = 500–1000 cells from four to six wing discs). AC values were normalized to 100%. Mann Whitney test was used to determine statistical significance comparing experimental and control (α-CatR) discs. ****(P≤0.0001), *(P = .0258). (G) Jub::GFP expression in control and Vinc null mutant (Vinc102.1/Vinc102.1) late 3rd larval wing discs. (H) vinc null mutant and control late 3rd larval wing discs have the same size. Two-tailed, unpaired t-test; ns (P>0.05) (I) Quantification of Jub::GFP fluorescent intensities (arbitrary units) in control and vinc null mutant discs (N>900 cells from five wing discs).