Fig 3. Phylogenetic analysis of HPC229 plasmid relaxases.
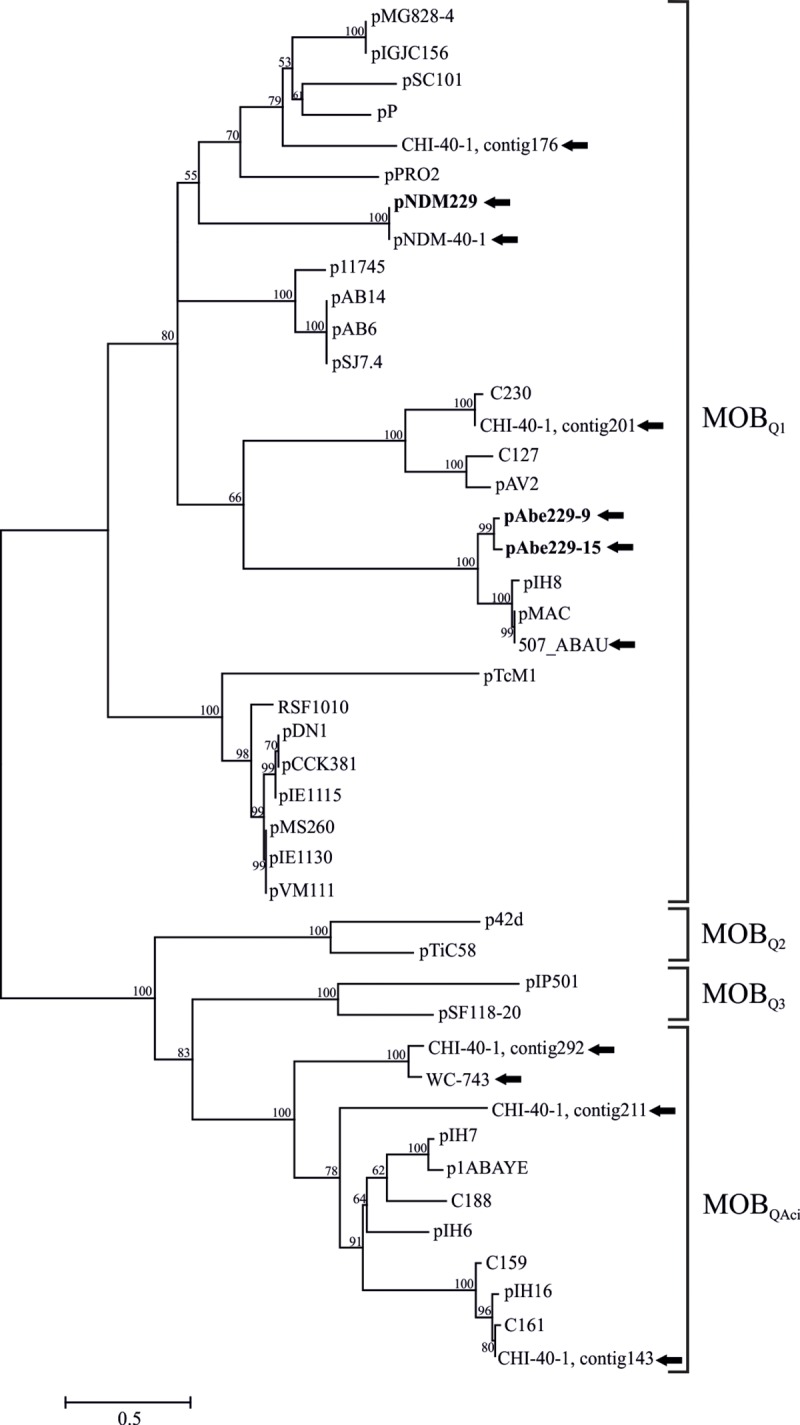
A ML tree was inferred from the alignments of the first 300 amino acids of the N-terminal domains of MOBQ relaxases from A. bereziniae and the Acinetobacter local database [3,30]. The MOBQ1, MOBQ2, MOBQ3 and MOBQAci sub-families are indicated. Relaxases encoded in A. bereziniae genomes are specified with black arrows, and those corresponding to HPC229 plasmids are additionally highlighted in bold. In the case of the CHI-40-1 draft genome (GenBank accession number CDEL01000000.1), the contig number in which a given relaxase gene was identified is additionally indicated. The evolutionary scale (number of amino acid substitution per site) is indicated at the botton left. Bootstrap values higher than 50% (100 replications) are indicated at the branching nodes of the ML tree.
