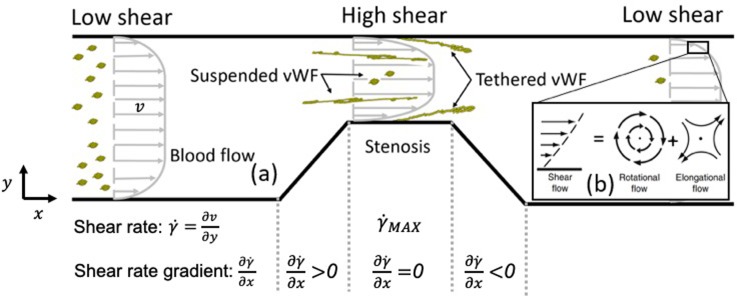
FIG. 6.
(a) Blood flow through a stenotic channel. The velocity profile is blunt due to the presence of red blood cells (RBCs). The stenosis region generates a high shear rate at the wall, leading to unfolding and potential tethering of plasma vWF near the wall. Tethered vWF gets fully stretched. (b) Shear flow can be theoretically decomposed into a rotational flow component and an elongational flow component.