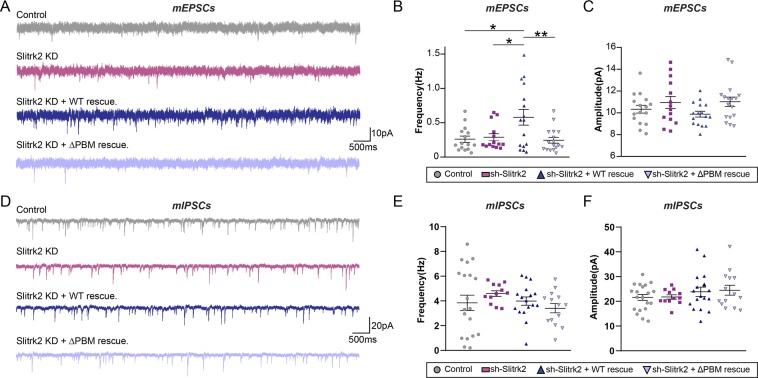
Figure 6.
Slitrk2 acts through its C-terminal PDZ-mediated interactions to promote excitatory synaptic transmission in CA1 hippocampal pyramidal neurons in vivo. (A–C) Representative traces (A) and summary graphs showing the frequency (B) and amplitude (C) of mEPSCs recorded from hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons infected with the indicated AAVs. Bar graphs show means ± SEMs (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01; non-parametric Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn’s post hoc test; ‘n’ denotes the total number of neurons analyzed as follows: Ctrl, n = 15 cells from 8 mice; Slitrk2 KD, n = 14 cells from 7 mice; Slitrk2 KD + WT rescue, n = 16 cells from 6 mice; Slitrk2 KD + ΔPBM rescue, n = 17 cells from 7 mice). (D–F) Representative traces (D) and summary graphs showing the frequency (E) and amplitude (F) of mIPSCs recorded from hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons infected with the indicated AAVs. Graphs show means ± SEMs (non-parametric Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn’s post hoc test; ‘n’ denotes the total number of neurons analyzed as follows: Ctrl, n = 20 cells from 5 mice; Slitrk2 KD, n = 12 cells from 5 mice; Slitrk2 KD + WT rescue, n = 17 cells from 5 mice; Slitrk2 KD + ΔPBM rescue, n = 14 cells from 4 mice).