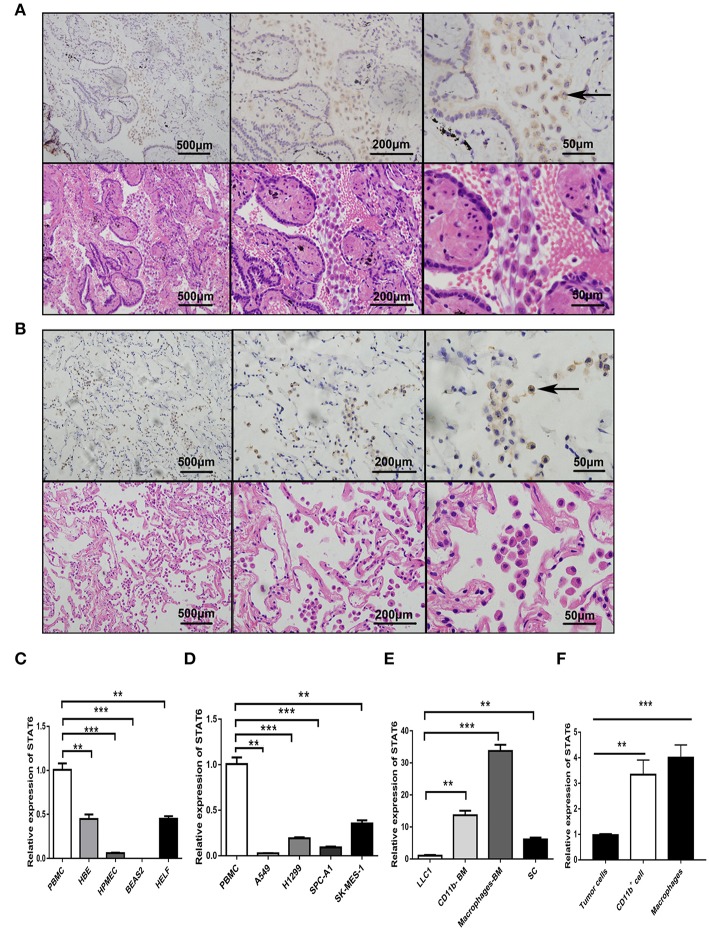
Figure 1.
Expression of signal transducer and activator of transcription 6 (STAT6) in lung cancer cells. (A) Immunohistochemical (IHC) staining of STAT6 in lung squamous carcinoma and corresponding hematoxylin and eosin (H&E)-stained images. (B) IHC staining of STAT6 in lung adenoma carcinoma and corresponding H&E-stained images. (C) Comparison of STAT6 mRNA expression between peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) and human-derived lung cells. Human-derived lung cell lines bought from ATCC, including normal human bronchial epithelial (HBE), human pulmonary microvascular endothelial cell (HPMEC), human embryonic lung fibroblast (HELF), and human bronchial cell line BEAS2. (D) Comparison of STAT6 mRNA expression between PBMC cells and lung cancer-derived cell lines. (E) Comparison of STAT6 mRNA expression between immune cells and tumor cells. Spleen cells (SC) were obtained from 6-week old BALB/c mice and removed red blood cells. CD11b+ cells and macrophage cells were obtained from bone marrow-derived cells of the same mice after removing red blood cells. (F) Comparison of STAT6 mRNA expression between cells. Tumor cells separated from primary tumor tissue induced by urethane, and CD11b+ cells and macrophages from the bone marrow of WT mice after urethane inoculation (at time point of 6 months). Data are presented as mean ± SD of one representative experiment. Similar results were seen in three independent experiments. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.