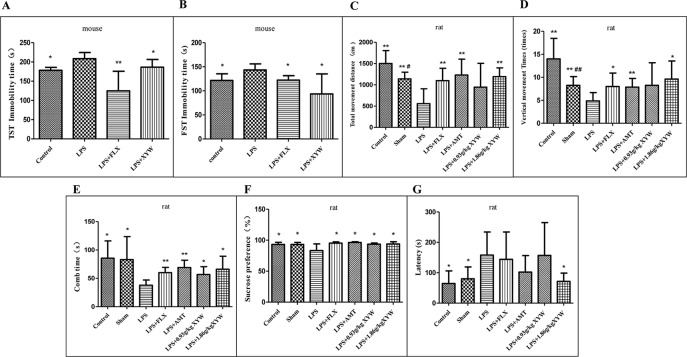
Figure 2.
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) administration acutely induced depression-like behavior. (A) Mice, the immobility time of the mice was prolonged in LPS group, compared with the control group (208.50 ± 15.90 vs 178.24 ± 7.62, N = 6 vs 5) (P 0.05), with 2 weeks of prior Xiaoyao Pills (XYW) administration (LPS + XYW), exhibited significantly lower immobility in the tail suspension test (208.50 ± 15.90 vs 186.38 ± 19.96, N = 6) (P 0.05) (Mann-Whitney test). (B) Mice, the immobility time of the mice was prolonged in LPS group, compared with the control group (143.39 ± 12.67 vs 121.55 ± 13.92, N = 6) (P 0.05), with 2 weeks of prior XYW administration (LPS + XYW), demonstrated significantly lower immobility in the forced swim test (143.39 ± 12.67 vs 93.56 ± 41.73, N = 6) (P 0.05) (t-test). (C, D) Rats, exposed to LPS exhibited significantly less distance travelled (558.75 ± 348.28 vs 1502.50 ± 303.73 (control) vs 1141.25 ± 156.79 (sham), N = 8) (P 0.05) and fewer number of vertical movements than the control and sham groups (4.88 ± 1.81 vs 14.00 ± 4.47 (control)vs 8.25 ± 1.91 (sham), N = 8) (P 0.05), with 2 weeks of prior XYW administration (LPS + XYW), exhibited a significantly higher distance travelled (558.75 ± 348.28 vs 945.00 ± 561.12 (0.93 g/kg) vs 1193.75 ± 204.80 (1.86 g/kg), N = 8) and times of vertical movement (4.88 ± 1.81 vs 8.25 ± 4.92 (0.93 g/kg) vs 9.63 ± 3.93 (1.86 g/kg), N = 8) (P 0.01) (t-test). (E) Rats, the LPS group exhibited a significantly lower comb time than the control and sham groups (37.88 ± 9.22 vs 85.50 ± 30.44 (control) vs 83.00 ± 40.62 (sham), N = 8) (P 0.05), with 2 weeks of prior XYW administration (LPS + XYW), exhibited a significantly longer time of combing (37.88 ± 9.22 vs 56.75 ± 13.77 (0.93 g/kg) vs 66.00 ± 22.90 (1.86 g/kg), N = 8) (n = 8, P 0.01) (Mann-Whitney test). (F) Rats, exposed to LPS exhibited a significantly lower saccharin preference than the control and sham groups [83.36 ± 10.72 vs 93.18 ± 3.44 (control) vs 93.25 ± 3.23 (sham), N = 8] (P 0.05), with 2 weeks of prior XYW administration (LPS + XYW), exhibited a significantly higher sucrose preference (83.36 ± 10.72 vs 93.62 ± 1.77 (0.93 g/kg) vs 93.91 ± 3.55 (1.86 g/kg), N = 8 vs 7 vs 8) (P 0.05) (t-test). (G) Rats, the LPS group exhibited a significantly longer latency to feed than the control and sham groups (158.00 ± 76.04 vs 64.63 ± 41.43 (control) vs 80.00 ± 39.14 (sham), N = 8) (P 0.05), with 2 weeks of prior XYW administration (LPS + XYW), exhibited a significantly shorter latency to feed (158.00 ± 76.04 vs 156.75 ± 108.30 (0.93 g/kg) vs 71.50 ± 27.40 (1.86 g/kg), N = 8) (n ≥ 7, P 0.05) (Mann-Whitney test). Compared with the control group, # P < 0.05,## P < 0.01. Compared with the LPS group, *P < 0.05,**P < 0.01.