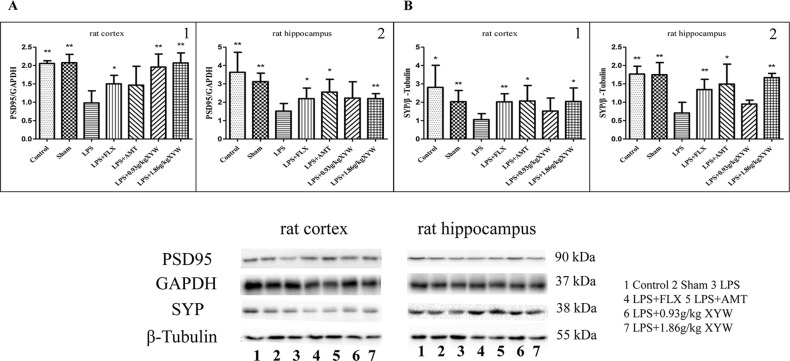
Figure 6.
LPS administration acutely reduced postsynaptic density protein 95 (PSD)-95 and synaptophysin (SYP) in different brain regions. (A, B) Rats, PSD95 (cortex:0.98 ± 0.33 vs 2.05 ± 0.08 (control) vs 2.08 ± 0.23 (sham), N = 6, hippocampus: 1.52 ± 0.41 vs 3.63 ± 1.09 (control) vs 3.12 ± 0.46 (sham), N = 6) and SYP (cortex:1.05 ± 0.33 vs 2.81 ± 1.20 (control) vs 2.03 ± 0.61 (sham), N = 6, hippocampus: 0.71 ± 0.29 vs 1.77 ± 0.21 (control) vs 1.75 ± 0.33 (sham), N = 6) were lower in the hippocampus and cortex in LPS treated group than the control (P 0.05 or P 0.01). with 2 weeks of prior XYW administration (LPS + XYW [1.86 g·kg-1]), exhibited a significantly higher level of PSD-95 and SYP in the cortex and hippocampus. 0.93 g·kg-1 Xiaoyao Pills also increased PSD-95 protein in the cortex (PSD-95: cortex:0.98 ± 0.33 vs 1.96 ± 0.35 (0.93 g/kg) vs 2.07 ± 0.27 (1.86 g/kg), N = 6, hippocampus: 1.52 ± 0.41 vs 2.23 ± 0.89 (0.93 g/kg) vs 2.20 ± 0.27 (1.86 g/kg), N = 6) (SYP: cortex: 1.05 ± 0.33 vs 1.52 ± 0.71 (0.93 g/kg) vs 2.04 ± 0.73 (1.86 g/kg), N = 6, hippocampus: 0.71 ± 0.29 vs 0.95 ± 0.11 (0.93 g/kg) vs 1.67 ± 0.12 (1.86 g/kg), N = 6) (P 0.05 or P 0.01) (A1: Mann-Whitney test, A2, B1-2: t-test). Compared with the LPS group, *P < 0.05,**P < 0.01.