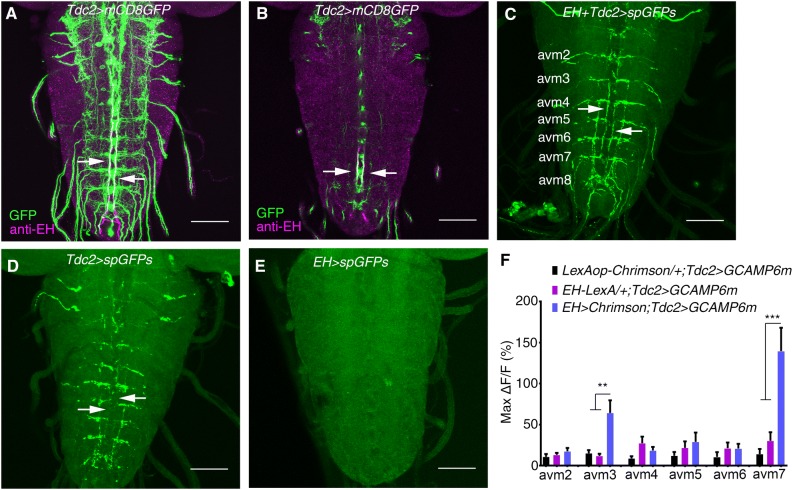
Fig. 3.
EH neurons innervate Tdc2 motor neurons. A Stacked image of co-staining of Tdc2-Gal4 marked by GFP and anti-EH in the larval VNC (green, GFP signal; magenta, anti-EH signal; arrows indicate co-localization. B Single layer view of (A). Arrows indicate co-localization. C–E GRASP between EH neurons and Tdc2 motor neurons (C). The GFP signal is seen where the axonal termini of EH neurons and the dendrites of Tdc2 motor neurons overlap, as indicated by arrows. D, E GRASP control in which split GFP expression was driven by Tdc2-Gal4 (D) and EH-LexA (E). No GFP signal for GRASP was seen (arrows). F Statistics of the peak Ca2+ response in cell bodies of Tdc2 motor neurons upon optogenetic activation of EH neurons (**P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, one-way ANOVA and post hoc Tukey’s multiple comparison test; no other significant differences between the experimental and control groups. See Fig. S4 for details. Scale bars, 50 μm in A–E.