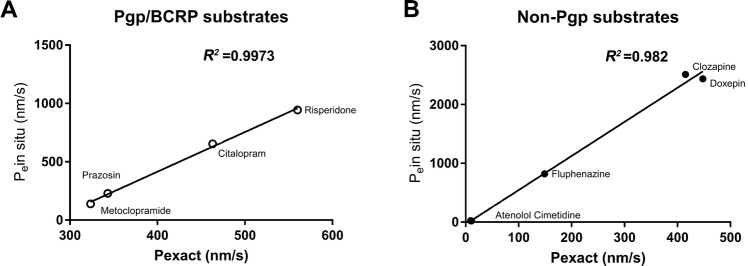
Fig. 6. Characterization of drug permeability in the hiPSC-derived in vitro BBB model.
. All transport studies performed across the in vitro BBB model used an optimized condition with rat primary glial co-culture. Correlations between the permeability coefficients of the drugs tested across the in vitro BBB model [Pexact (nm/s)] and the apparent permeability coefficients of the same drugs measured in rodent models Pe by in situ brain perfusion (nm/s) (Table 2). Three passages of iPSC-derived ECs were used in the experiments (n = 6/passage). A Linear coefficient of correlation R2 = 0.9973 for the Pgp substrate drugs risperidone, citalopram, prazosin, and metoclopramide (Prism XY correlation analysis Y = 3.4*X – 945; where X is the Pexact obtained from our assay result) (Table 2). B Linear coefficient of correlation R2 = 0.982 for the non-Pgp substrates (including passive-diffusion drugs and weak Pgp/BCRP substrate drugs) clozapine, doxepin, fluphenazine, altenolol, and cimetidine (Prism XY correlation analysis Y = 5.8*X − 35.37; where X is the Pexact obtained from our assay result) (Table 2).